1.1 第一个里程碑:安装sersync软件
1.1.1 将软件上传到服务器当中并解压
1、上传软件到服务器上 rz -E
为了便于管理上传位置统一设置为 /server/tools 中
2、解压软件包
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 |
[root@backup sersync_installdir_64bit]# tree
.
└── sersync
├── bin
│ └── sersync
├── conf
│ └── confxml.xml
└── logs |
1.1.2 二进制包安装方法
二进制包安装软件方法(绿色软件安装方法):
直接解压就可以使用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 |
[root@nfs01 sersync_installdir_64bit]# mv sersync/ /usr/local/
[root@nfs01 tools]# tree /usr/local/sersync/
/usr/local/sersync/
├── bin
│ └── sersync
├── conf
│ └── confxml.xml
└── logs
directories, 2 files |
1.2 第二个里程碑:编写sersync配置文件
1.2.1 常见的语法格式
rsync 配置文件编写:ini语法
sersync配置文件编写:xml语法
ansible配置文件编写:yml 语法
1.2.2 修改配置文件
编写前备份
|
1
2
3
4 |
[root@backup conf]# ll
total 4
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2214 Oct 26 2011 confxml.xml
[root@backup conf]# cp confxml.xml{,.bak} |
6-11行表示排除同步的数据,等价于 –exclude 功能,表示排除
|
1
2
3
4
5
6 |
<filter start="false">
<exclude expression="(.*)\\.svn"></exclude>
<exclude expression="(.*)\\.gz"></exclude>
<exclude expression="^info/*"></exclude>
<exclude expression="^static/*"></exclude>
</filter> |
12-21行是利用inotify的功能监控指定的事件,等价与 -e create,delete…… 表示指定监控事件信息
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10 |
<inotify>
<delete start="true"/>
<createFolder start="true"/>
<createFile start="false"/>
<closeWrite start="true"/>
<moveFrom start="true"/>
<moveTo start="true"/>
<attrib start="false"/>
<modify start="false"/>
</inotify> |
24-28行:推送到哪里 name=模块 是rsync服务器的地址
|
1
2
3
4
5 |
<localpath watch="/data"> #监控那个目录
<remote ip="172.16.1.41" name="backup"/>
<!--<remote ip="192.168.8.39" name="tongbu"/>-->
<!--<remote ip="192.168.8.40" name="tongbu"/>-->
</localpath> |
29-35行 定义rsync推送时的参数信息。
注意:不要有单词拼写错误 (true),否则程序不能正常启动,卡死
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 |
<rsync>
<commonParams params="-az"/>
<auth start="true" users="rsync_backup" passwordfile="/etc/rsync.password"/>
<userDefinedPort start="false" port="874"/><!-- port=874 -->
<timeout start="false" time="100"/><!-- timeout=100 -->
<ssh start="false"/>
</rsync> |
配置文件最终内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67 |
[root@nfs01 tools]# cat /usr/local/sersync/conf/confxml.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<head version="2.5">
<host hostip="localhost" port="8008"></host>
<debug start="false"/>
<fileSystem xfs="false"/>
<filter start="false">
<exclude expression="(.*)\\.svn"></exclude>
<exclude expression="(.*)\\.gz"></exclude>
<exclude expression="^info/*"></exclude>
<exclude expression="^static/*"></exclude>
</filter>
<inotify>
<delete start="true"/>
<createFolder start="true"/>
<createFile start="false"/>
<closeWrite start="true"/>
<moveFrom start="true"/>
<moveTo start="true"/>
<attrib start="false"/>
<modify start="false"/>
</inotify>
<sersync>
<localpath watch="/data">
<remote ip="172.16.1.41" name="nfsbackup"/>
<!--<remote ip="192.168.8.39" name="tongbu"/>-->
<!--<remote ip="192.168.8.40" name="tongbu"/>-->
</localpath>
<rsync>
<commonParams params="-az"/>
<auth start="true" users="rsync_backup" passwordfile="/etc/rsync.password"/>
<userDefinedPort start="false" port="874"/><!-- port=874 -->
<timeout start="false" time="100"/><!-- timeout=100 -->
<ssh start="false"/>
</rsync>
<failLog path="/tmp/rsync_fail_log.sh" timeToExecute="60"/><!--default every 60mins execute once-->
<crontab start="false" schedule="600"><!--600mins-->
<crontabfilter start="false">
<exclude expression="*.php"></exclude>
<exclude expression="info/*"></exclude>
</crontabfilter>
</crontab>
<plugin start="false" name="command"/>
</sersync>
<plugin name="command">
<param prefix="/bin/sh" suffix="" ignoreError="true"/> <!--prefix /opt/tongbu/mmm.sh suffix-->
<filter start="false">
<include expression="(.*)\\.php"/>
<include expression="(.*)\\.sh"/>
</filter>
</plugin>
<plugin name="socket">
<localpath watch="/opt/tongbu">
<deshost ip="192.168.138.20" port="8009"/>
</localpath>
</plugin>
<plugin name="refreshCDN">
<localpath watch="/data0/htdocs/cms.xoyo.com/site/">
<cdninfo domainname="ccms.chinacache.com" port="80" username="xxxx" passwd="xxxx"/>
<sendurl base="http://pic.xoyo.com/cms"/>
<regexurl regex="false" match="cms.xoyo.com/site([/a-zA-Z0-9]*).xoyo.com/images"/>
</localpath>
</plugin>
</head> |
1.3 第三里程碑: 启动sersync
1.3.1 修改文件的权限(可执行)
首先让程序让文件有执行权限
|
1
2
3
4 |
[root@nfs01 bin]# chmod a+x sersync
[root@nfs01 bin]# ll
total 1768
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 1810128 Oct 26 2011 sersync |
1.3.2 查看软件的帮助信息
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 |
[root@nfs01 bin]# ./sersync -h
set the system param
execute:echo 50000000 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
execute:echo 327679 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events
parse the command param
_______________________________________________________
重要参数-d:启用守护进程模式
重要参数-r:在监控前,将监控目录与远程主机用rsync命令推送一遍
参数-n: 指定开启守护线程的数量,默认为10个
重要参数-o:指定配置文件,默认使用confxml.xml文件
参数-m:单独启用其他模块,使用 -m refreshCDN 开启刷新CDN模块
参数-m:单独启用其他模块,使用 -m socket 开启socket模块
参数-m:单独启用其他模块,使用 -m http 开启http模块
不加-m参数,则默认执行同步程序
________________________________________________________________ |
1.3.3 在程序的bin目录下启动程序
|
1 |
./sersync -dro /usr/local/sersync/conf/confxml.xml |
1.3.4 启动方法二
将/usr/local/sersync/bin/程序的bin目录添加到PATH中
|
1 |
export PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin:/usr/local/sersync/bin/ |
然后sersync命令就能直接使用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26 |
[root@nfs01 scripts]# sersync -dro /usr/local/sersync/conf/confxml.xml
set the system param
execute:echo 50000000 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
execute:echo 327679 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events
parse the command param
option: -d run as a daemon
option: -r rsync all the local files to the remote servers before the sersync work
option: -o config xml name: /usr/local/sersync/conf/confxml.xml
daemon thread num: 10
parse xml config file
host ip : localhost host port: 8008
daemon start,sersync run behind the console
use rsync password-file :
user is rsync_backup
passwordfile is /etc/rsync.password
config xml parse success
please set /etc/rsyncd.conf max connections=0 Manually
sersync working thread 12 = 1(primary thread) + 1(fail retry thread) + 10(daemon sub threads)
Max threads numbers is: 22 = 12(Thread pool nums) + 10(Sub threads)
please according your cpu ,use -n param to adjust the cpu rate
------------------------------------------
rsync the directory recursivly to the remote servers once
working please wait...
execute command: cd /data && rsync -az -R --delete ./ rsync_backup@172.16.1.41::nfsbackup --password-file=/etc/rsync.password >/dev/null 2>&1
run the sersync:
watch path is: /data |
1.4 Inotify与 sersync总结对比
1.4.1 Inotify实时并发:
结论:经过测试,每秒200文件并发,数据同步几乎无延迟(小于1秒)
1.4.2 inotify 优点:
1)监控文件系统事件变化,通过同步工具实现实时数据同步。
1.4.3 inotify 缺点
1)并发如果大于200个文件(10-100k),同步就会有延迟
2)我们前面写的脚本,每次都是全部推送一次,但确实是增量的。也可以只同步变化的文件,不变化的不理。
3)监控到事件后,调用rsync同步是单进程的,而sersync为多进程同步。既然有了inotify-tools,为什么还要开发sersync?
1.4.4 serysync功能多:(inotify+rsync命令)
1)支持通过配置文件管理
2)真正的守护进程socket
3)可以对失败文件定时重传(定时任务功能)
4)第三方的HTTP接口(例如:更新cdn缓存)
5)默认多进程rsync同步
1)inotify(sersync)+ rsync,是文件级别的。
2)drbd文件系统级别,文件系统级别,基于block块同步,缺点:备节点数据不可用
3)第三方软件的同步功能:mysql同步(主从复制),oracle,mongodb
4)程序双写,直接写两台服务器。
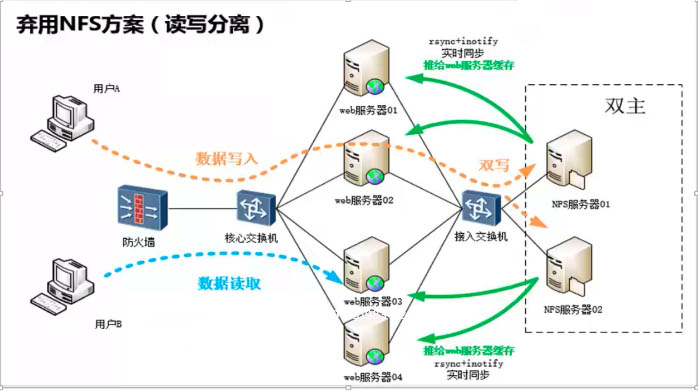
5)利用产品业务逻辑解决(读写分离,备份读不到,读主)
2.1 man命令的级别
centos6
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 |
[root@nfs01 ~]# man man
The standard sections of the manual include:
User Commands #用户命令
System Calls #系统调用
C Library Functions # Ç库函数
Devices and Special Files #设备和特殊文件
File Formats and Conventions #文件格式和约定
Games et. Al. #游戏等。
Miscellanea #杂记
System Administration tools and Daemons #系统管理工具和程序
Distributions customize the manual section to their specifics,
which often include additional sections. |
centos7
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11 |
[root@clsn tuichu]# man ~
Executable programs or shell commands
System calls (functions provided by the kernel)
Library calls (functions within program libraries)
Special files (usually found in /dev)
File formats and conventions eg /etc/passwd
Games
Miscellaneous (including macro packages and conventions), e.g.
man(7), groff(7)
System administration commands (usually only for root)
Kernel routines [Non standard] |
以上这篇sersync实现数据实时同步的方法就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持快网idc。
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/clsn/p/7707828.html
相关文章
- 服务器技术之硬件冗余技术 2025-05-27
- 服务器是租用还是服务器托管好? 2025-05-27
- 什么是DNS以及它如何影响服务器? 2025-05-27
- 刀片服务器与机架服务器的区别介绍 2025-05-27
- 服务器虚拟化技术深度科普 2025-05-27
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
-
2025-05-26 96
-
2025-05-26 65
-
2025-05-27 89
-
2025-05-27 58
-
2025-05-27 50