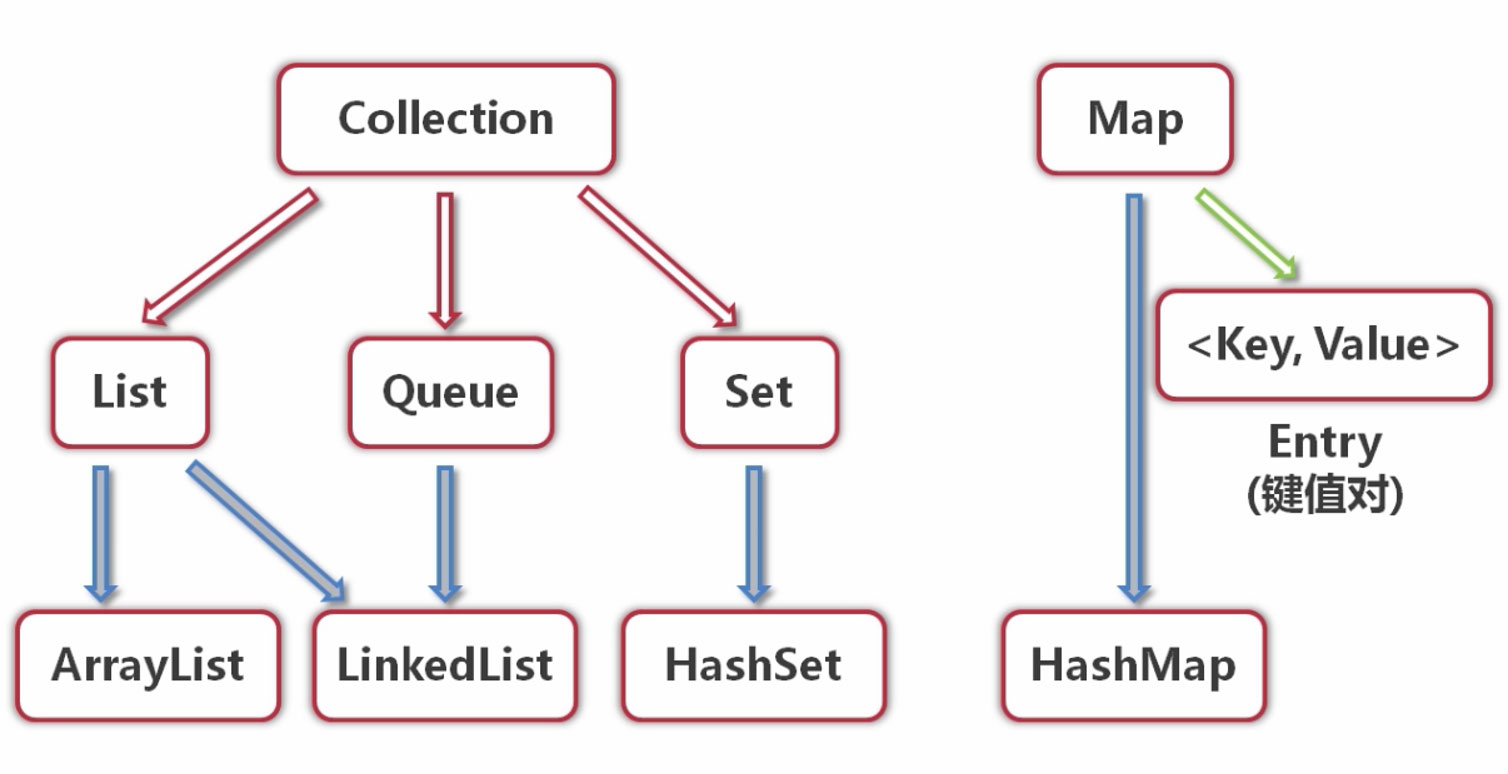
概念
java中的集合类:是一种工具类,就像是容器,储存任意数量的具有共同属性的对象
集合的作用
集合框架的类型:
collection和map 都是接口,不能实例化
list和queue有序、可重复,set无序、不可重复
list添加元素两种add方法
1、直接添加,元素添加在队尾;
对象存入集合都变成object类型,取出时需要类型转换
2、指定位置添加,指定的位置(从0开始)不能超过队列的长度,否则报错(数组下标越界)。
list的两种addall方法:添加类的数组
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public void testadd(){
//add方法一
course cr1 = new course("1", "课程一");
coursestoselect.add(cr1);
course temp = (course)coursestoselect.get(0);
system.out.println("添加了课程:"+temp.id+":"+temp.name);
//add方法二,添加到指定位置
course cr2 = new course("2", "课程二");
coursestoselect.add(0, cr2);;
course temp2 = (course)coursestoselect.get(0);
system.out.println("添加了课程:"+temp2.id+":"+temp2.name);
//addall数组添加方法一
course[] cr34 = {new course("3", "课程三"), new course("4", "课程四")};
coursestoselect.addall(arrays.aslist(cr34));//添加数组的方法
course temp3 = (course)coursestoselect.get(2);
course temp4 = (course)coursestoselect.get(3);
system.out.println("添加了两门课程:"+temp3.id+":"+temp3.name+
";"+temp4.id+":"+temp4.name);
//addall数组添加方法二,添加到指定位置
course[] cr56 = {new course("5", "课程五"), new course("6", "课程六")};
coursestoselect.addall(2, arrays.aslist(cr56));
course temp5 = (course)coursestoselect.get(2);
course temp6 = (course)coursestoselect.get(3);
system.out.println("添加了两门课程:"+temp5.id+":"+temp5.name+
";"+temp6.id+":"+temp6.name);
}
|
遍历list
1.for循环遍历
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
/**
* 取得list中的元素的方法
* @param args
*/
public void testget(){
int size = coursestoselect.size();
system.out.println("有如下课程待选:");
for(int i=0; i<size;i++){
course cr = (course)coursestoselect.get(i);
system.out.println("课程:"+cr.id+":"+cr.name);
}
}
|
2.通过迭代器来遍历list,迭代器只是用来遍历集合中元素的,本身不具有存储元素的功能。可以说它是依赖某个集合存在的,不能独立存在。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
/**
* 通过迭代器来遍历list
* @param args
*/
public void testiterator(){
iterator it = coursestoselect.iterator();
system.out.println("有如下课程待选(迭代器):");
while(it.hasnext()){
course cr = (course)it.next();//iterator的next方法
system.out.println("课程:"+cr.id+":"+cr.name);
}
}
|
3.通过for each 方法访问集合元素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
/**
* 通过for each 方法访问集合元素
* @param args
*/
public void testforeach(){
system.out.println("有如下课程待选(for each):");
for(object obj:coursestoselect){
course cr = (course)obj;//取出的元素一致都为object类型,需要强转
system.out.println("课程:"+cr.id+":"+cr.name);
}
}
|
修改list中的元素。list中有个set方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
/**
* 修改list中的元素
* @param args
*/
public void testmodify(){
coursestoselect.set(4, new course("7", "课程七"));
}
|
删除list中的元素。与add相似,有remove和removeall两种
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
/**
* 删除list中的元素
* @param args
*/
public void testremore(){
course cr = (course)coursestoselect.get(4);
system.out.println("我是课程:"+cr.id+":"+cr.name+",我即将被删除了");
coursestoselect.remove(cr);
system.out.println("删掉了。。");
testforeach();//方法内部调用方法
}
|
上述remove()中也可直接放入索引下标,即可直接删除。如remove(4)
removeall是从一个集合中将另一个集合中的所有元素全部删除。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public void testremore(){
course[] courses={(course)coursestoselect.get(3),(course)coursestoselect.get(4)};
system.out.println("我是课程:3,4,我即将被删除了");
coursestoselect.removeall(arrays.aslist(courses));
system.out.println("删掉了。。");
testforeach();//方法内部调用方法
}
|
**实际编写代码中最好每个类中的属性都私有(private),需要使用时再用getxx或setxx
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
private string id;
public string getid(){
return id;
}
public string setid(){
this.id=id;
}
|
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作能带来一定的帮助,同时也希望多多支持快网idc!
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/atingjia/p/6479888.html
相关文章
- 个人网站服务器域名解析设置指南:从购买到绑定全流程 2025-06-10
- 个人网站搭建:如何挑选具有弹性扩展能力的服务器? 2025-06-10
- 个人服务器网站搭建:如何选择适合自己的建站程序或框架? 2025-06-10
- 64M VPS建站:能否支持高流量网站运行? 2025-06-10
- 64M VPS建站:怎样选择合适的域名和SSL证书? 2025-06-10
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
-
Linux Kernel 5.10.1紧急发布:修复两处存储代码BUG
2025-05-27 101 -
2025-05-27 87
-
2025-05-29 69
-
2025-06-04 65
-
2025-05-29 42