缘起
一切都源于我的上一篇博客,我写的是一篇 uitableviewcell使用自动布局的“最佳实践” ,我需要给我的图片里面的uiview元素添加上边距的标记,这让我感到很为难,我觉得我得发点时间写一个程序让这个步骤自动化,我只要一键就能让我的程序自动标记边距,这个比我要手动去标记来的酷很多不是吗!
结果
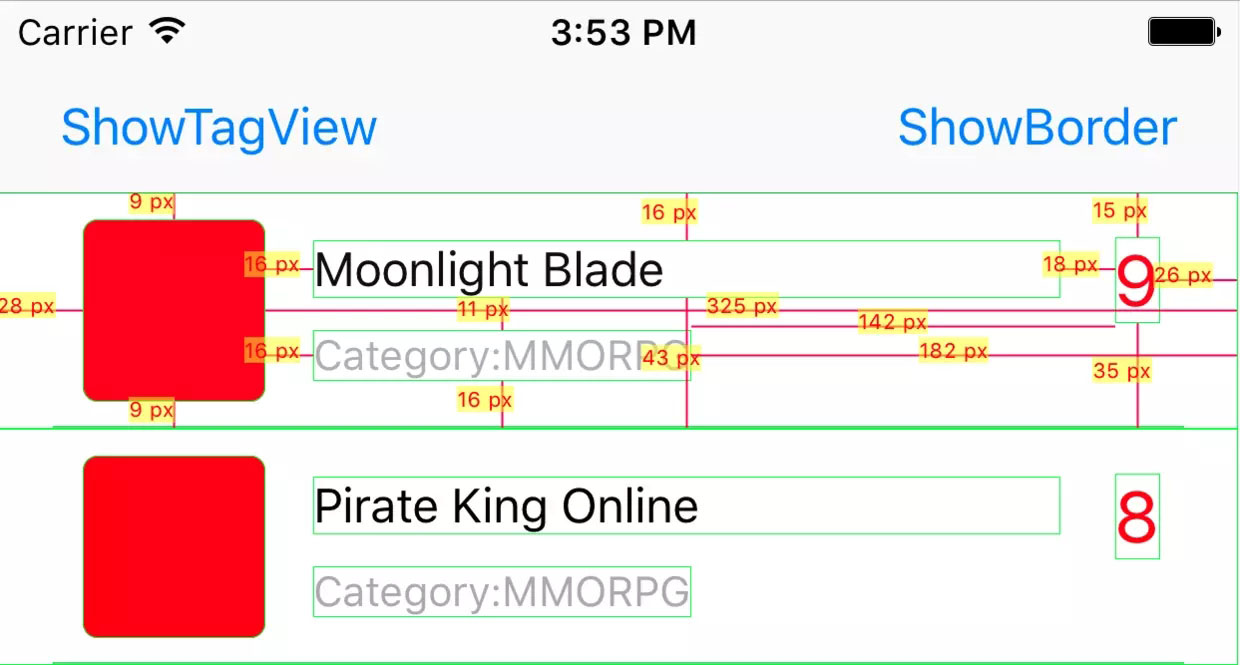
所以,我发了点时间实现了我的想法,下面是实现的结果截图:
以及代码开源托管地址:代码链接
预览图
过去几小时内的想法
静下心来整理我的想法和寻找方案,大概的整理下了一个可行性的方案以及这个方案中需要使用到的步骤,其中一些细节没有在这个步骤中体现
- 获取水平的间距:遍历父view的子view,获取某个子sourceview的右边到其他子targetview的左边的距离,把结果保存到子targetview的入度数组中
- 获取垂直的间距:遍历父view的子view,获取某个子sourceview的下边到其他子targetview的上边的距离,把结果保存到子targetview的入度数组中
- 筛选出targetview的入度数组中所以不符合的结果,删除这些结果
- 最终获取到了一个需要进行展示的结果数组,数组保存的是一系列的间距线段对象
- 创建一个显示标记的tagview层,把结果的线段绘制在tagview上面,然后把tabview添加到父view上
代码实现解析
注入测试边框view
我的方案中所有的间距都是基于子view考虑的,所以子view和父view的边距需要特殊的计算,可以使用在父view的旁边添加一个物理像素的子view,最终只要处理所有这些子view,子view和父view的边距就能得到体现了,不用再做多余的处理,这是一个讨巧的方案。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
+ (void)registerbordertestviewwithview:(uiview*)view {
cgfloat minwh = 1.0/[uiscreen mainscreen].scale;
mmborderattachview* leftborderview = [[mmborderattachview alloc] initwithframe:cgrectmake(0, 0, minwh, view.bounds.size.height)];
[view addsubview:leftborderview];
mmborderattachview* rightborderview = [[mmborderattachview alloc] initwithframe:cgrectmake(view.bounds.size.width-minwh, 0, minwh, view.bounds.size.height)];
[view addsubview:rightborderview];
mmborderattachview* topborderview = [[mmborderattachview alloc] initwithframe:cgrectmake(0, 0, view.bounds.size.width, minwh)];
[view addsubview:topborderview];
mmborderattachview* bottomborderview = [[mmborderattachview alloc] initwithframe:cgrectmake(0, view.bounds.size.height - minwh, view.bounds.size.width, minwh)];
[view addsubview:bottomborderview];
}
|
获取父view的所有子view,抽象为mmframeobject对象
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
nsmutablearray* viewframeobjs = [nsmutablearray array];
nsarray* subviews = view.subviews;
for (uiview* subview in subviews) {
// 过滤特殊的view,不属于注入的view
if (![subview conformstoprotocol:@protocol(mmabstractview)]) {
if (subview.alpha<0.001f) {
continue;
}
if (subview.frame.size.height <= 2) {
continue;
}
}
mmframeobject* frameobj = [[mmframeobject alloc] init];
frameobj.frame = subview.frame;
frameobj.attachedview = subview;
[viewframeobjs addobject:frameobj];
}
|
获取view之间的间距
需要处理两种情况:1、寻找view的右边对应的其他view的左边;2、寻找view的下边对应的其他view的上边,特殊滴需要处理两者都是mmabstractview的情况,这种不需要处理
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
nsmutablearray<mmline*>* lines = [nsmutablearray array];
for (mmframeobject* sourceframeobj in viewframeobjs) {
for (mmframeobject* targetframeobj in viewframeobjs) {
// 过滤特殊的view
if ([sourceframeobj.attachedview conformstoprotocol:@protocol(mmabstractview)]
&& [targetframeobj.attachedview conformstoprotocol:@protocol(mmabstractview)]) {
continue;
}
// 寻找view的右边对应的其他view的左边
mmline* hline = [self horizontallinewithframeobj1:sourceframeobj frameobj2:targetframeobj];
if (hline) {
[lines addobject:hline];
[targetframeobj.leftinjectedobjs addobject:hline];
}
// 寻找view的下边对应的其他view的上边
mmline* vline = [self verticallinewithframeobj1:sourceframeobj frameobj2:targetframeobj];
if (vline) {
[lines addobject:vline];
[targetframeobj.topinjectedobjs addobject:vline];
}
}
}
|
获取间距线段的实现
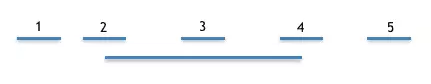
以获取水平的间距线段为例,这种情况,只需要处理一个子view在另一个子view的右边的情况,否则返回nil跳过。获取水平间距线段,明显的线段的x轴是确定的,要,只要处理好y轴就行了,问题就抽象为了两个线段的问题,这部分是在approperiatepointwithinternal方法中处理的,主要步骤是一长的线段为标准,然后枚举短的线段和长的线段存在的5种情况,相应的计算合适的值,然后给y轴使用。
两条线段的5种关系
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
|
+ (mmline*)horizontallinewithframeobj1:(mmframeobject*)frameobj1 frameobj2:(mmframeobject*)frameobj2 {
if (abs(frameobj1.frame.origin.x - frameobj2.frame.origin.x) < 3) {
return nil;
}
// frameobj2整体在frameobj1右边
if (frameobj1.frame.origin.x + frameobj1.frame.size.width >= frameobj2.frame.origin.x) {
return nil;
}
cgfloat obj1rightx = frameobj1.frame.origin.x + frameobj1.frame.size.width;
cgfloat obj1height = frameobj1.frame.size.height;
cgfloat obj2leftx = frameobj2.frame.origin.x;
cgfloat obj2height = frameobj2.frame.size.height;
cgfloat handle = 0;
cgfloat pointy = [self approperiatepointwithinternal:[[mminterval alloc] initwithstart:frameobj1.frame.origin.y length:obj1height] internal2:[[mminterval alloc] initwithstart:frameobj2.frame.origin.y length:obj2height] handle:&handle];
mmline* line = [[mmline alloc] initwithpoint1:[[mmshortpoint alloc] initwithx:obj1rightx y:pointy handle:handle] point2:[[mmshortpoint alloc] initwithx:obj2leftx y:pointy handle:handle]];
return line;
}
+ (cgfloat)approperiatepointwithinternal:(mminterval*)internal1 internal2:(mminterval*)internal2 handle:(cgfloat*)handle {
cgfloat minhandlevalue = 20;
cgfloat pointvalue = 0;
cgfloat handlevalue = 0;
mminterval* biginternal;
mminterval* smallinternal;
if (internal1.length > internal2.length) {
biginternal = internal1;
smallinternal = internal2;
} else {
biginternal = internal2;
smallinternal = internal1;
}
// 线段分割法
if (smallinternal.start < biginternal.start && smallinternal.start+smallinternal.length < biginternal.start) {
cgfloat tmphandlevalue = biginternal.start - smallinternal.start+smallinternal.length;
pointvalue = biginternal.start - tmphandlevalue/2;
handlevalue = max(tmphandlevalue, minhandlevalue);
}
if (smallinternal.start < biginternal.start && smallinternal.start+smallinternal.length >= biginternal.start) {
cgfloat tmphandlevalue = smallinternal.start+smallinternal.length - biginternal.start;
pointvalue = biginternal.start + tmphandlevalue/2;
handlevalue = max(tmphandlevalue, minhandlevalue);
}
if (smallinternal.start >= biginternal.start && smallinternal.start+smallinternal.length <= biginternal.start+biginternal.length) {
cgfloat tmphandlevalue = smallinternal.length;
pointvalue = smallinternal.start + tmphandlevalue/2;
handlevalue = max(tmphandlevalue, minhandlevalue);
}
if (smallinternal.start >= biginternal.start && smallinternal.start+smallinternal.length > biginternal.start+biginternal.length) {
cgfloat tmphandlevalue = biginternal.start+biginternal.length - smallinternal.start;
pointvalue = biginternal.start + tmphandlevalue/2;
handlevalue = max(tmphandlevalue, minhandlevalue);
}
if (smallinternal.start >= biginternal.start+biginternal.length && smallinternal.start+smallinternal.length > biginternal.start+biginternal.length) {
cgfloat tmphandlevalue = smallinternal.start - (biginternal.start+biginternal.length);
pointvalue = smallinternal.start - tmphandlevalue/2;
handlevalue = max(tmphandlevalue, minhandlevalue);
}
if (handle) {
*handle = handlevalue;
}
return pointvalue;
}
|
过滤线段
一个子view对象的入度可能有好几个,需要筛选进行删除,我使用的筛选策略是:以水平的间距线段为例,两条线段的y差值小于某个阈值,选择线段长的那条删除,最终获取到了一个需要进行展示的结果数组,数组保存的是一系列的间距线段对象
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
// 查找重复的射入line
// hline:y的差值小于某个值,leftinjectedobjs->取最小一条
// vline:x的差值小于某个值,topinjectedobjs->取最小一条
cgfloat minvalue = 5;
for (mmframeobject* sourceframeobj in viewframeobjs) {
{
// 排序:y值:从大到小
[sourceframeobj.leftinjectedobjs sortusingcomparator:^nscomparisonresult(mmline* _nonnull obj1, mmline* _nonnull obj2) {
return obj1.point1.point.y > obj2.point1.point.y;
}];
int i = 0;
nslog(@"\\n\\n");
mmline* baseline, *compareline;
if (sourceframeobj.leftinjectedobjs.count) {
baseline = sourceframeobj.leftinjectedobjs[i];
}
while (i<sourceframeobj.leftinjectedobjs.count) {
nslog(@"linewidth = %.1f == ", baseline.linewidth);
if (i + 1 < sourceframeobj.leftinjectedobjs.count) {
compareline = sourceframeobj.leftinjectedobjs[i + 1];
if (abs(baseline.point1.point.y - compareline.point1.point.y) < minvalue) {
// 移除长的一条
if (baseline.linewidth > compareline.linewidth) {
[lines removeobject:baseline];
baseline = compareline;
} else {
[lines removeobject:compareline];
}
} else {
baseline = compareline;
}
}
i++;
}
}
{
// 排序:x值从大到小
[sourceframeobj.topinjectedobjs sortusingcomparator:^nscomparisonresult(mmline* _nonnull obj1, mmline* _nonnull obj2) {
return obj1.point1.point.x >
obj2.point1.point.x;
}];
int j = 0;
mmline* baseline, *compareline;
if (sourceframeobj.topinjectedobjs.count) {
baseline = sourceframeobj.topinjectedobjs[j];
}
while (j<sourceframeobj.topinjectedobjs.count) {
if (j + 1 < sourceframeobj.topinjectedobjs.count) {
compareline = sourceframeobj.topinjectedobjs[j + 1];
if (abs(baseline.point1.point.x - compareline.point1.point.x) < minvalue) {
// 移除长的一条
// 移除长的一条
if (baseline.linewidth > compareline.linewidth) {
[lines removeobject:baseline];
baseline = compareline;
} else {
[lines removeobject:compareline];
}
} else {
baseline = compareline;
}
}
j++;
}
}
}
|
tagview 的绘制
|
1
2
3
|
// 绘制view
taggingview* taggingview = [[taggingview alloc] initwithframe:view.bounds lines:lines];
[view addsubview:taggingview];
|
taggingview 在drawrect绘制线段以及线段长度的文字
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
//
// taggingview.m
// autolayoutcell
//
// created by aron on 2017/5/27.
// copyright © 2017年 aron. all rights reserved.
//
#import "taggingview.h"
#import "mmtagmodel.h"
@interface taggingview ()
@property (nonatomic, strong) nsarray<mmline*>* lines;;
@end
@implementation taggingview
- (instancetype)initwithframe:(cgrect)frame lines:(nsarray<mmline*>*)lines {
self = [super initwithframe:frame];
if (self) {
self.backgroundcolor = [uicolor colorwithred:255 green:255 blue:255 alpha:0.05];
_lines = lines;
}
return self;
}
- (void)drawrect:(cgrect)rect {
[super drawrect:rect];
//1.获取上下文
cgcontextref context = uigraphicsgetcurrentcontext();
for (mmline* line in _lines) {
// 绘制线段
cgcontextsetlinewidth(context, 2.0f/[uiscreen mainscreen].scale); //线宽
cgcontextsetallowsantialiasing(context, true);
cgcontextsetrgbstrokecolor(context, 255.0 / 255.0, 0.0 / 255.0, 70.0 / 255.0, 1.0); //线的颜色
cgcontextbeginpath(context);
//设置起始点
cgcontextmovetopoint(context, line.point1.point.x, line.point1.point.y);
//增加点
cgcontextaddlinetopoint(context, line.point2.point.x, line.point2.point.y);
cgcontextstrokepath(context);
// 绘制文字
nsstring *string = [nsstring stringwithformat:@"%.0f px", line.linewidth];
uifont *fount = [uifont systemfontofsize:7];
cgpoint centerpoint = line.centerpoint;
nsdictionary* attrdict = @{nsfontattributename : fount,
nsforegroundcolorattributename: [uicolor redcolor],
nsbackgroundcolorattributename: [uicolor colorwithred:1 green:1 blue:0 alpha:0.5f]};
[string drawinrect:cgrectmake(centerpoint.x - 15, centerpoint.y - 6, 30, 16) withattributes:attrdict];
}
}
@end
|
以上就是我的的思路以及实现,有什么好的建议希望可以收到issue一起交流和谈论。
代码托管位置
代码传送门
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,谢谢大家对快网idc的支持。
相关文章
- ASP.NET自助建站系统中的用户注册和登录功能定制方法 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统的域名绑定与解析教程 2025-06-10
- 个人服务器网站搭建:如何选择合适的服务器提供商? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统中如何实现多语言支持? 2025-06-10
- 64M VPS建站:如何选择最适合的网站建设平台? 2025-06-10
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
-
2025-05-29 105
-
2025-05-27 64
-
2025-05-29 94
-
2025-05-29 68
-
2025-05-29 17