最近看android framework层代码,看到了threadlocal这个类,有点儿陌生,就翻了各种相关博客一一拜读;自己随后又研究了一遍源码,发现自己的理解较之前阅读的博文有不同之处,所以决定自己写篇文章说说自己的理解,希望可以起到以下作用:
– 可以疏通研究结果,加深自己的理解;
– 可以起到抛砖引玉的作用,帮助感兴趣的同学疏通思路;
– 分享学习经历,同大家一起交流和学习。
一、 threadlocal 是什么
threadlocal 是java类库的基础类,在包java.lang下面;
官方的解释是这样的:
implements a thread-local storage, that is, a variable for which each thread has its own value. all threads share the same threadlocal object, but each sees a different value when accessing it, and changes made by one thread do not affect the other threads. the implementation supports null values.
大致意思是:
可以实现线程的本地存储机制,threadlocal变量是一个不同线程可以拥有不同值的变量。所有的线程可以共享同一个threadlocal对象,但是不同线程访问的时候可以取得不同的值,而且任意一个线程对它的改变不会影响其他线程。类实现是支持null值的(可以在set和get方法传递和访问null值)。
概括来讲有三个特性:
– 不同线程访问时取得不同的值
– 任意线程对它的改变不影响其他线程
– 支持null
下面分别对这些特性进行实例验证,首先定义一个test类,在此类中我们鉴证上边所提到的三个特性。类定义如下:
test.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
public class test{
//定义threadlocal
private static threadlocal name;
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception{
name = new threadlocal();
//define thread a
thread a = new thread(){
public void run(){
system.out.println("before invoke set,value is:"+name.get());
name.set(“thread a”);
system.out.println("after invoke set, value is:"+name.get());
}
}
;
//define thread b
thread b = new thread(){
public void run(){
system.out.println("before invoke set,value is :"+name.get());
name.set(“thread b”);
system.out.println("after invoke set,value is :"+name.get());
}
}
;
// not invoke set, print the value is null
system.out.println(name.get());
// invoke set to fill a value
name.set(“thread main”);
// start thread a
a.start();
a.join();
// print the value after changed the value by thread a
system.out.println(name.get());
// start thread b
b.start();
b.join();
// print the value after changed the value by thread b
system.out.println(name.get())
}
}
|
代码分析:
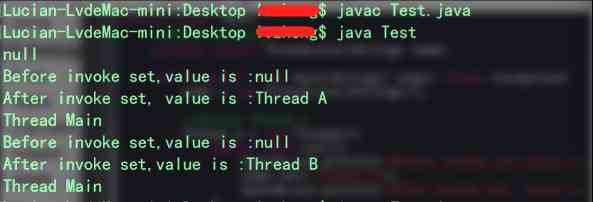
从定义中我们可以看到只声明了一个threadlocal对象,其他三个线程(主线程、thread a和thread b)共享同一个对象;然后,在不同的线程中修改对象的值和在不同的线程中访问对象的值,并在控制台输出查看结果。
看结果:
从控制台输出结果可以看到里边有三个null的输出,这个是因为在输出前没有对对象进行赋值,验证了支持null的特点;再者,还可以发现在每个线程我都对对象的值做了修改,但是在其他线程访问对象时并不是修改后的值,而是访问线程本地的值;这样也验证了其他两个特点。
二、 threadlocal的作用
大家都知道它的使用场景大都是多线程编程,至于具体的作用,这个怎么说那?我觉得这个只能用一个泛的说法来定义,因为一个东西的功能属性定义了以后会限制大家的思路,就好比说菜刀是用来切菜的,好多人就不会用它切西瓜了。
这里,说下我对它的作用的认识,仅供参考,希望能有所帮助。这样来描述吧,当一个多线程的程序需要对多数线程的部分任务(就是run方法里的部分代码)进行封装时,在封装体里就可以用threadlocal来包装与线程相关的成员变量,从而保证线程访问的独占性,而且所有线程可以共享一个封装体对象;可以参考下android里的looper。不会用代码描述问题的程序员不是好程序员;
看代码:统计线程某段代码耗时的工具(为说明问题自造)
statisticcosttime.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
// class that statistic the cost time
public class statisticcosttime{
// record the starttime
// private threadlocal starttime = new threadlocal();
private long starttime;
// private threadlocal costtime = new threadlocal();
private long costtime;
private statisticcosttime(){
}
//singleton
public static final statisticcosttime shareinstance(){
return instancefactory.instance;
}
private static class instancefactory{
private static final statisticcosttime instance = new statisticcosttime();
}
// start
public void start(){
// starttime.set(system. nanotime ());
starttime = system.nanotime();
}
// end
public void end(){
// costtime.set(system. nanotime () - starttime.get());
costtime = system.nanotime() - starttime;
}
public long getstarttime(){
return starttime;
// return starttime.get();
}
public long getcosttime(){
// return costtime.get();
return costtime;
}
|
好了,工具设计完工了,现在我们用它来统计一下线程耗时试试呗:
main.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
public class main{
public static void main(string[] args) throws exception{
// define the thread a
thread a = new thread(){
public void run(){
try{
// start record time
statisticcosttime.shareinstance().start();
sleep(200);
// print the start time of a
system.out.println("a-starttime:"+statisticcosttime.shareinstance().getstarttime());
// end the record
statisticcosttime.shareinstance().end();
// print the costtime of a
system.out.println("a:"+statisticcosttime.shareinstance().getcosttime());
}
catch(exception e){
}
}
}
;
// start a
a.start();
// define thread b
thread b = new thread(){
public void run(){
try{
// record the start time of b1
statisticcosttime.shareinstance().start();
sleep(100);
// print the start time to console
system.out.println("b1-starttime:"+statisticcosttime.shareinstance().getstarttime());
// end record start time of b1
statisticcosttime.shareinstance().end();
// print the cost time of b1
system.out.println("b1:"+statisticcosttime.shareinstance().getcosttime());
// start record time of b2
statisticcosttime.shareinstance().start();
sleep(100);
// print start time of b2
system.out.println("b2-starttime:"+statisticcosttime.shareinstance().getstarttime());
// end record time of b2
statisticcosttime.shareinstance().end();
// print cost time of b2
system.out.println("b2:"+statisticcosttime.shareinstance().getcosttime());
}
catch(exception e){
}
}
}
;
b.start();
}
}
|
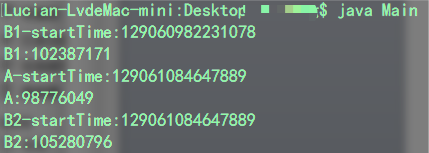
运行代码后输出结果是这样的
注意:输出结果精确度为纳秒级
看结果是不是和我们预想的不一样,发现a的结果应该约等于b1+b2才对呀,怎么变成和b2一样了那?答案就是我们在定义starttime和costtime变量时,本意是不应共享的,应是线程独占的才对。而这里变量随单例共享了,所以当计算a的值时,其实starttime已经被b2修改了,所以就输出了和b2一样的结果。
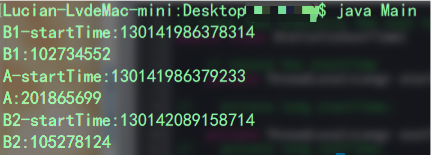
现在我们把statisticcosttime中注释掉的部分打开,换成threadlocal的声明方式试下。
看结果:
呀!这下达到预期效果了,这时候有同学会说这不是可以线程并发访问了吗,是不是只要我用了threadlocal就可以保证线程安全了?答案是no!首先先弄明白为什么会有线程安全问题,无非两种情况:
1、不该共享的资源,你在线程间共享了;
2、线程间共享的资源,你没有保证有序访问;
前者可以用“空间换时间”的方式解决,用threadlocal(也可以直接声明线程局部变量),后者用“时间换空间”的方式解决,显然这个就不是threadlocal力所能及的了。
三、 threadlocal 原理
实现原理其实很简单,每次对threadlocal 对象的读写操作其实是对线程的values对象的读写操作;这里澄清一下,没有什么变量副本的创建,因为就没有用变量分配的内存空间来存t对象的,而是用它所在线程的values来存t对象的;我们在线程中每次调用threadlocal的set方法时,实际上是将object写入线程对应values对象的过程;调用threadlocal的get方法时,实际上是从线程对应values对象取object的过程。
看源码:
threadlocal 的成员变量set
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
/**
* sets the value of this variable for the current thread. if set to
* {@code null}, the value will be set to null and the underlying entry will
* still be present.
*
* @param value the new value of the variable for the caller thread.
*/
public void set(t value) {
thread currentthread = thread.currentthread();
values values = values(currentthread);
if (values == null) {
values = initializevalues(currentthread);
}
values.put(this, value);
}
|
treadlocal 的成员方法get
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
/**
* returns the value of this variable for the current thread. if an entry
* doesn't yet exist for this variable on this thread, this method will
* create an entry, populating the value with the result of
* {@link #initialvalue()}.
*
* @return the current value of the variable for the calling thread.
*/
@suppresswarnings("unchecked")
public t get() {
// optimized for the fast path.
thread currentthread = thread.currentthread();
values values = values(currentthread);
if (values != null) {
object[] table = values.table;
int index = hash & values.mask;
if (this.reference == table[index]) {
return (t) table[index + 1];
}
} else {
values = initializevalues(currentthread);
}
return (t) values.getaftermiss(this);
}
|
threadlocal的成员方法initializevalues
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
/**
* creates values instance for this thread and variable type.
*/
values initializevalues(thread current) {
return current.localvalues = new values();
}
|
threadlocal 的成员方法values
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
/**
* gets values instance for this thread and variable type.
*/
values values(thread current) {
return current.localvalues;
}
|
那这个values又是怎样读写object那?
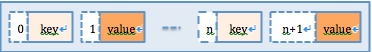
values是作为threadlocal的内部类存在的;这个values里包括了一个重要数组object[],这个数据就是解答问题的关键部分,它是用来存储线程本地各种类型treadlocal变量用的;那么问题来了,具体取某个类型的变量时是怎么保证不取到其他类型的值那?按一般的做法会用一个map根据key-value映射一下的;对的,思路就是这个思路,但是这里并没有用map来实现,是用一个object[]实现的map机制;但是,若要用map理解的话,也是不可以的,因为机制是相同的;key其实上对应threadlocal的弱引用,value就对应我们传进去的object。
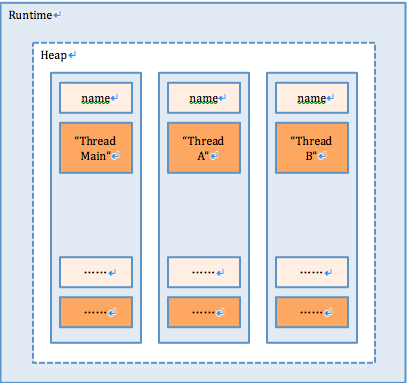
解释下是怎么用object[]实现map机制的(参考图1);它是用数组下标的奇偶来区分key和value的,就是下表是偶数的位置存储key,奇数存储value,就是这样搞得;感兴趣的同学如果想知道算法实现的话,可以深入研究一下,这里我不在详述了。
结合前面第一个实例分析下存储情况:
当程序执行时存在a,b和main三个线程,分别在线程中调用name.set()时同时针对三个线程实例在堆区分配了三块相同的内存空间来存储values对象,以name引用作为key,具体的object作为值存进三个不同的object[](参看下图):
四、 总结
threadlocal 不能完全解决多线程编程时的并发问题,这种问题还要根据不同的情况选择不同的解决方案,“空间换时间”还是“时间换空间”。
threadlocal最大的作用就是把线程共享变量转换成线程本地变量,实现线程之间的隔离。
以上就是本文关于快速了解java中threadlocal的全部内容,希望对大家有所帮助。如有不足之处,欢迎留言指出。感谢朋友们对本站的支持。
原文链接:https://www.2cto.com/kf/201608/541771.html
相关文章
- 64M VPS建站:如何选择最适合的网站建设平台? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET本地开发时常见的配置错误及解决方法? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统的数据库备份与恢复操作指南 2025-06-10
- 个人网站服务器域名解析设置指南:从购买到绑定全流程 2025-06-10
- 个人网站搭建:如何挑选具有弹性扩展能力的服务器? 2025-06-10
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
-
2025-05-27 68
-
2025-05-25 71
-
2025-05-29 100
-
2025-06-04 23
-
2025-05-25 84