java中树的存储结构实现 一、树 树与线性表、栈、队列等线性结构不同,树是一…节点与节点之间的父子关系,可以为每个节点增加一个parent域,用以记录该节点的父点
树是一种抽象数据类型(adt)或是实作这种抽象数据类型的数据结构,用来模拟具有树状结构性质的数据集合。它是由n(n>0)个有限节点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。把 它叫做“树”是因为它看起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的。
树定义和基本术语
定义
树(tree)是n(n≥0)个结点的有限集t,并且当n>0时满足下列条件:
(1)有且仅有一个特定的称为根(root)的结点;
(2)当n>1时,其余结点可以划分为m(m>0)个互不相交的有限集t1、t2、…、tm,每个集ti(1≤i≤m)均为树,且称为树t的子树(subtree)。
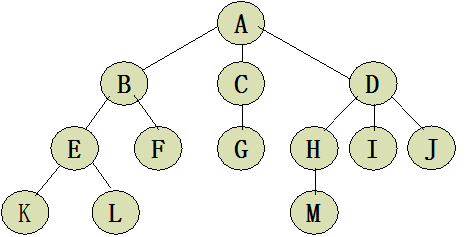
如下就是一棵树的结构:
基本术语
结点:存储数据元素和指向子树的链接,由数据元素和构造数据元素之间关系的引用组成。
孩子结点:树中一个结点的子树的根结点称为这个结点的孩子结点,如图1中的a的孩子结点有b、c、d
双亲结点:树中某个结点有孩子结点(即该结点的度不为0),该结点称为它孩子结点的双亲结点,也叫前驱结点。双亲结点和孩子结点是相互的,如图1中,a的孩子结点是b、c、d,b、c、d的双亲结点是a。
兄弟结点:具有相同双亲结点(即同一个前驱)的结点称为兄弟结点,如图1中b、b、d为兄弟结点。
结点的度:结点所有子树的个数称为该结点的度,如图1,a的度为3,b的度为2.
树的度:树中所有结点的度的最大值称为树的度,如图1的度为3.
叶子结点:度为0的结点称为叶子结点,也叫终端结点。如图1的k、l、f、g、m、i、j
分支结点:度不为0的结点称为分支结点,也叫非终端结点。如图1的a、b、c、d、e、h
结点的层次:从根结点到树中某结点所经路径的分支数称为该结点的层次。根结点的层次一般为1(也可以自己定义为0),这样,其它结点的层次是其双亲结点的层次加1.
树的深度:树中所有结点的层次的最大值称为该树的深度(也就是最下面那个结点的层次)。
有序树和无序树:树中任意一个结点的各子树按从左到右是有序的,称为有序树,否则称为无序树。
树的抽象数据类型描述
数据元素:具有相同特性的数据元素的集合。
结构关系:树中数据元素间的结构关系由树的定义确定。
基本操作:树的主要操作有
(1)创建树inttree(&t)
创建1个空树t。
(2)销毁树destroytree(&t)
(3)构造树creattree(&t,deinition)
(4)置空树cleartree(&t)
将树t置为空树。
(5)判空树treeempty(t)
(6)求树的深度treedepth(t)
(7)获得树根root(t)
(8)获取结点value(t,cur_e,&e)
将树中结点cur_e存入e单元中。
(9)数据赋值assign(t,cur_e,value)
将结点value,赋值于树t的结点cur_e中。
(10)获得双亲parent(t,cur_e)
返回树t中结点cur_e的双亲结点。
(11)获得最左孩子leftchild(t,cur_e)
返回树t中结点cur_e的最左孩子。
(12)获得右兄弟rightsibling(t,cur_e)
返回树t中结点cur_e的右兄弟。
(13)插入子树insertchild(&t,&p,i,c)
将树c插入到树t中p指向结点的第i个子树之前。
(14)删除子树deletechild(&t,&p,i)
删除树t中p指向结点的第i个子树。
(15)遍历树traversetree(t,visit())
树的实现
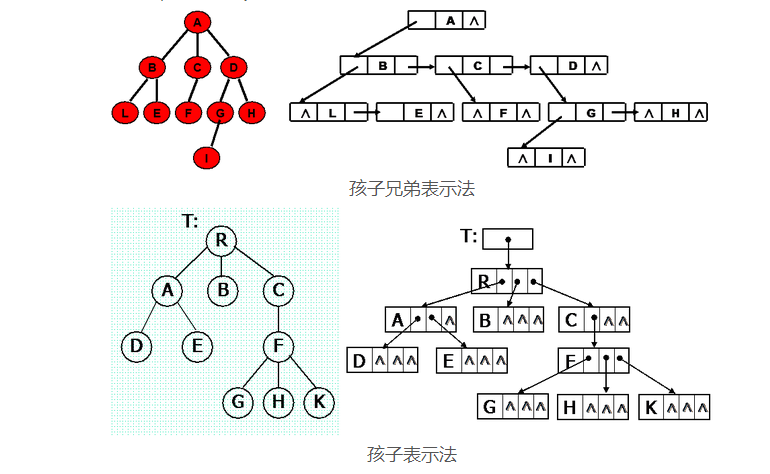
树是一种递归结构,表示方式一般有孩子表示法和孩子兄弟表示法两种。树实现方式有很多种、有可以由广义表的递归实现,也可以有二叉树实现,其中最常见的是将树用孩子兄弟表示法转化成二叉树来实现。
下面以孩子表示法为例讲一下树的实现:
树的定义和实现
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
|
package datastructure.tree;
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.arrays;
import java.util.linkedlist;
import java.util.list;
/**
* 树的定义和实现
* @author administrator
*
*/
public class tree {
private object data;
private list<tree> childs;
public tree(){
data = null;
childs = new arraylist();
childs.clear();
}
public tree(object data) {
this.data = data;
childs = new arraylist();
childs.clear();
}
/**
* 添加子树
* @param tree 子树
*/
public void addnode(tree tree) {
childs.add(tree);
}
/**
* 置空树
*/
public void cleartree() {
data = null;
childs.clear();
}
/**
* 求树的深度
* 这方法还有点问题,有待完善
* @return 树的深度
*/
public int dept() {
return dept(this);
}
/**
* 求树的深度
* 这方法还有点问题,有待完善
* @param tree
* @return
*/
private int dept(tree tree) {
if(tree.isempty()) {
return 0;
} else if(tree.isleaf()) {
return 1;
} else {
int n = childs.size();
int[] a = new int[n];
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
if(childs.get(i).isempty()) {
a[i] = 0+1;
} else {
a[i] = dept(childs.get(i)) + 1;
}
}
arrays.sort(a);
return a[n-1];
}
}
/**
* 返回递i个子树
* @param i
* @return
*/
public tree getchild(int i) {
return childs.get(i);
}
/**
* 求第一个孩子 结点
* @return
*/
public tree getfirstchild() {
return childs.get(0);
}
/**
* 求最后 一个孩子结点
* @return
*/
public tree getlastchild() {
return childs.get(childs.size()-1);
}
public list<tree> getchilds() {
return childs;
}
/**
* 获得根结点的数据
* @return
*/
public object getrootdata() {
return data;
}
/**
* 判断是否为空树
* @return 如果为空,返回true,否则返回false
*/
public boolean isempty() {
if(childs.isempty() && data == null)
return true;
return false;
}
/**
* 判断是否为叶子结点
* @return
*/
public boolean isleaf() {
if(childs.isempty())
return true;
return false;
}
/**
* 获得树根
* @return 树的根
*/
public tree root() {
return this;
}
/**
* 设置根结点的数据
*/
public void setrootdata(object data) {
this.data = data;
}
/**
* 求结点数
* 这方法还有点问题,有待完善
* @return 结点的个数
*/
public int size() {
return size(this);
}
/**
* 求结点数
* 这方法还有点问题,有待完善
* @param tree
* @return
*/
private int size(tree tree) {
if(tree.isempty()) {
return 0;
} else if(tree.isleaf()) {
return 1;
} else {
int count = 1;
int n = childs.size();
for (int i=0; i<n; i++) {
if(!childs.get(i).isempty()) {
count += size(childs.get(i));
}
}
return count;
}
}
}
|
树的遍历
树的遍历有两种
前根遍历
(1).访问根结点;
(2).按照从左到右的次序行根遍历根结点的第一棵子树;
后根遍历
(1).按照从左到右的次序行根遍历根结点的第一棵子树;
(2).访问根结点;
visit.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
package datastructure.tree;
import datastructure.tree.btree.btree;
/**
* 对结点进行操作的接口,规定树的遍历的类必须实现这个接口
* @author administrator
*
*/
public interface visit {
/**
* 对结点进行某种操作
* @param btree 树的结点
*/
public void visit(btree btree);
}
|
order.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
package datastructure.tree;
import java.util.list;
/**
* 树的遍历
* @author administrator
*
*/
public class order {
/**
* 先根遍历
* @param root 要的根结点
*/
public void preorder(tree root) {
if(!root.isempty()) {
visit(root);
for (tree child : root.getchilds()) {
if(child != null) {
preorder(child);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 后根遍历
* @param root 树的根结点
*/
public void postorder(tree root) {
if(!root.isempty()) {
for (tree child : root.getchilds()) {
if(child != null) {
preorder(child);
}
}
visit(root);
}
}
public void visit(tree tree) {
system.out.print("\\t" + tree.getrootdata());
}
}
|
测试:
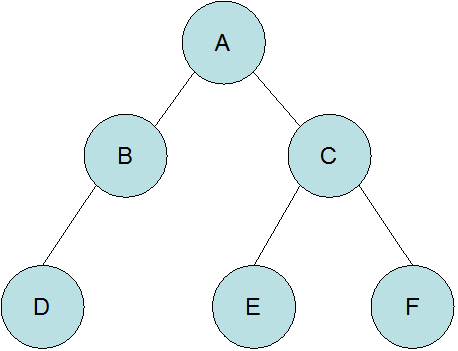
要遍历的树如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
package datastructure.tree;
import java.util.iterator;
import java.util.scanner;
public class treetest {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(string[] args) {
tree root = new tree("a");
root.addnode(new tree("b"));
root.addnode(new tree("c"));
root.addnode(new tree("d"));
tree t = null;
t = root.getchild(0);
t.addnode(new tree("l"));
t.addnode(new tree("e"));
t = root.getchild(1);
t.addnode(new tree("f"));
t = root.getchild(2);
t.addnode(new tree("i"));
t.addnode(new tree("h"));
t = t.getfirstchild();
t.addnode(new tree("l"));
system.out.println("first node:" + root.getrootdata());
//system.out.println("size:" + root.size());
//system.out.println("dept:" + root.dept());
system.out.println("is left:" + root.isleaf());
system.out.println("data:" + root.getrootdata());
order order = new order();
system.out.println("前根遍历:");
order.preorder(root);
system.out.println("\\n后根遍历:");
order.postorder(root);
}
}
|
结果:
first node:a
is left:false
data:a
前根遍历:
a bl e c f di l h
后根遍历:
b le c f d il h a
结束语:
以上就是本文关于java数据结构之树基本概念解析及代码示例的全部内容,希望对大家有所帮助。如有不足之处,欢迎留言指出。
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/web424/p/6911892.html
相关文章
- 个人服务器网站搭建:如何选择合适的服务器提供商? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统中如何实现多语言支持? 2025-06-10
- 64M VPS建站:如何选择最适合的网站建设平台? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET本地开发时常见的配置错误及解决方法? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统的数据库备份与恢复操作指南 2025-06-10
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
-
2025-05-29 57
-
2025-05-27 34
-
2025-05-27 59
-
2025-06-04 93
-
2025-06-04 91