本文研究的主要是spring事务隔离级别(solation level)介绍及例子,具体如下。
当两个事务对同一个数据库的记录进行操作时,那么,他们之间的影响是怎么样的呢?这就出现了事务隔离级别的概念。数据库的隔离性与并发控制有很大关系。数据库的隔离级别是数据库的事务特性acid的一部分。acid,即原子性(atomicity)、一致性(consistency)、隔离性(isolation)和持久性(durability)。spring的事务隔离级别有四个:read_uncommitted、read_committed、repeatable_read和serializable。还有一个,是数据库默认的隔离级别default,mysql默认是repeatable_read。
下面来具体看看。
read_uncommitted
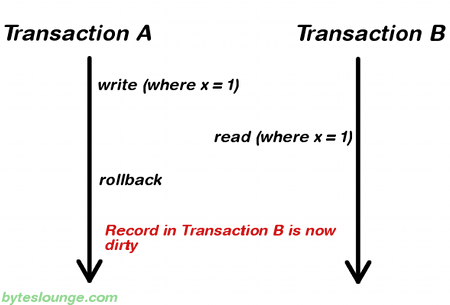
顾名思义,read_uncommitted意思是,一个事务可以读取到另一个事务未提交的事务记录。换句话说,a transaction can read the data that is still uncommitted by other transactions。这是spring事务最弱的隔离级别。见下面的图,事务a开启,写入一条记录,这时候,事务b读入数据,读到了这条记录,但是,之后事务a回滚。因此,事务b读到的数据不是有效的(the database is in an invalid state)。这种情况称为脏读(dirty read)。除了脏读的问题,read_uncommitted还可能出现non-repeatable read(不可重复读)和phantom read(幻读)的问题。
read_committed
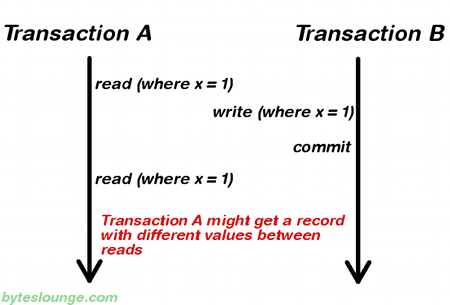
read_committed隔离级别表明,一个事务只能读取到已经提交的记录,不能读取到未提交的记录。换句话说,a transaction can only read the committed data, and it can't read the uncommitted data.因此,dirty read的情况不再发生,但可能会出现其他问题。见下图。
在事务a两次读取的过程之间,事务b修改了那条记录并进行提交。因此,事务a前后两次读取的记录不一致。这个问题称为non-repeatable read(不可重复读)。(两次读取的记录不一致,重复读取就会发现问题。)
除了non-repeatable read的问题,read_committed还可能发生phantom read的问题。
repeatable_read
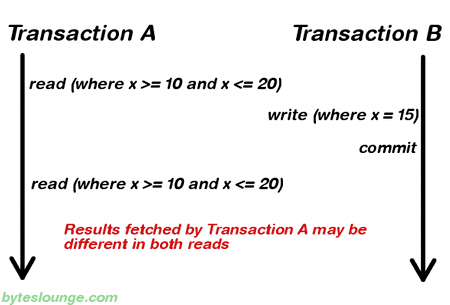
repeatable_read意思是,一个事务可以多次从数据库读取某条记录,而且多次读取的那条记录都是一致的,相同的。这个隔离级别可以避免dirty read和non-repeatable read的问题,但可能发生phantom read的问题。如下图。
事务a两次从数据库读取一系列记录,期间,事务b插入了某条记录并提交。事务a第二次读取时,会读取到事务b刚刚插入的那条记录。在事务期间,事务a两次读取的一系列记录不一致,这个问题称为phantom read。
serializable
serializable是spring最强的隔离级别。事务执行时,会在所有级别上加锁,比如read和write时都会加锁,仿佛事务是以串行的方式进行的,而不是一起发生的。这会防止dirty read、non-repeatable read和phantom read的出现,但是,会带来性能的下降。
default
mysql默认是repeatable_read。
例子
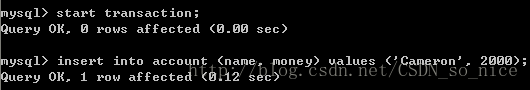
下面,我们看一个例子。在数据库mysql里开启一个事务,不提交。然后,另一个事务读取记录。
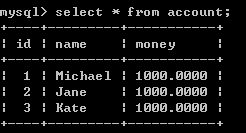
刚开始,数据库里的记录,如图
接下来,在数据库mysql中开启事务a,并插入一条记录。
在service的业务类的事务属性配置为read_uncommitted。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
@transactional(isolation=isolation.read_uncommitted)
public class accountservice {
private accountdao accountdao;
public accountdao getaccountdao() {
return accountdao;
}
public void setaccountdao(accountdao accountdao) {
this.accountdao = accountdao;
}
public void transfer(string from, string to, double money) {
accountdao.outmoney(from, money);
accountdao.inmoney(to, money);
}
public void readalluser() {
list<account> accounts = accountdao.getalluser();
for (account account : accounts) {
system.out.println(account);
}
}
}
|
运行下面的测试类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
package com.chris.service;
import static org.junit.assert.*;
import org.junit.test;
import org.junit.runner.runwith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.contextconfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.springjunit4classrunner;
@runwith(springjunit4classrunner.class)
@contextconfiguration("classpath:applicationcontext.xml")
public class readallusertest {
@autowired
private accountservice accountservice;
@test
public void test() {
accountservice.readalluser();
}
}
|
结果如下:
可见,这个事务读取到了未提交的数据。
这时候,将mysql中开启的事务a回滚。
|
1
|
mysql> rollback;
|
再次运行程序,结果为
account [name=michael, money=1000.0]
account [name=jane, money=1000.0]
account [name=kate, money=1000.0]
总结
以上就是本文关于spring事务隔离级别简介及实例解析的全部内容,希望对大家有所帮助。感兴趣的朋友可以继续参阅本站其他相关专题,如有不足之处,欢迎留言指出。感谢朋友们对本站的支持!
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/csdn_so_nice/article/details/54290665
相关文章
- 64M VPS建站:如何选择最适合的网站建设平台? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET本地开发时常见的配置错误及解决方法? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统的数据库备份与恢复操作指南 2025-06-10
- 个人网站服务器域名解析设置指南:从购买到绑定全流程 2025-06-10
- 个人网站搭建:如何挑选具有弹性扩展能力的服务器? 2025-06-10
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
-
2025-05-25 72
-
IOS开发之多线程NSThiread GCD NSOperation Runloop
2025-05-29 103 -
2025-06-04 81
-
2025-06-04 73
-
2025-05-27 102