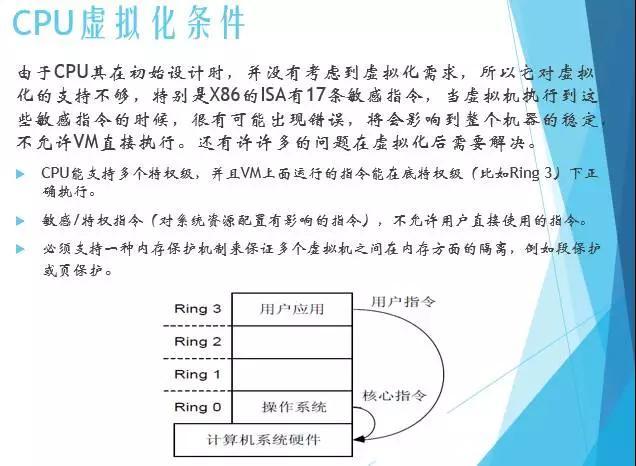
K-Means算法是一种基于距离的聚类算法,采用迭代的方法,计算出K个聚类中心,把若干个点聚成K类。
MLlib实现K-Means算法的原理是,运行多个K-Means算法,每个称为run,返回最好的那个聚类的类簇中心。初始的类簇中心,可以是随机的,也可以是KMean||得来的,迭代达到一定的次数,或者所有run都收敛时,算法就结束。
用Spark实现K-Means算法,首先修改pom文件,引入机器学习MLlib包:
?
|
1
2
3
4
5 |
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-mllib_2.10</artifactId>
<version>1.6.0</version>
</dependency> |
代码:
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45 |
import org.apache.log4j.{Level,Logger}
import org.apache.spark.{SparkContext, SparkConf}
import org.apache.spark.mllib.clustering.KMeans
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.Vectors
object Kmeans {
def main(args:Array[String]) = {
// 屏蔽日志
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.spark").setLevel(Level.WARN)
Logger.getLogger("org.apache.jetty.server").setLevel(Level.OFF)
// 设置运行环境
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("K-Means").setMaster("spark://master:7077")
.setJars(Seq("E:\\\\Intellij\\\\Projects\\\\SimpleGraphX\\\\SimpleGraphX.jar"))
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
// 装载数据集
val data = sc.textFile("hdfs://master:9000/kmeans_data.txt", 1)
val parsedData = data.map(s => Vectors.dense(s.split(" ").map(_.toDouble)))
// 将数据集聚类,2个类,20次迭代,形成数据模型
val numClusters = 2
val numIterations = 20
val model = KMeans.train(parsedData, numClusters, numIterations)
// 数据模型的中心点
println("Cluster centres:")
for(c <- model.clusterCenters) {
println(" " + c.toString)
}
// 使用误差平方之和来评估数据模型
val cost = model.computeCost(parsedData)
println("Within Set Sum of Squared Errors = " + cost)
// 使用模型测试单点数据
println("Vectors 7.3 1.5 10.9 is belong to cluster:" + model.predict(Vectors.dense("7.3 1.5 10.9".split(" ")
.map(_.toDouble))))
println("Vectors 4.2 11.2 2.7 is belong to cluster:" + model.predict(Vectors.dense("4.2 11.2 2.7".split(" ")
.map(_.toDouble))))
println("Vectors 18.0 4.5 3.8 is belong to cluster:" + model.predict(Vectors.dense("1.0 14.5 73.8".split(" ")
.map(_.toDouble))))
// 返回数据集和结果
val result = data.map {
line =>
val linevectore = Vectors.dense(line.split(" ").map(_.toDouble))
val prediction = model.predict(linevectore)
line + " " + prediction
}.collect.foreach(println)
sc.stop
}
} |
使用textFile()方法装载数据集,获得RDD,再使用KMeans.train()方法根据RDD、K值和迭代次数得到一个KMeans模型。得到KMeans模型以后,可以判断一组数据属于哪一个类。具体方法是用Vectors.dense()方法生成一个Vector,然后用KMeans.predict()方法就可以返回属于哪一个类。
运行结果:
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16 |
Cluster centres:
[6.062499999999999,6.7124999999999995,11.5]
[3.5,12.2,60.0]
Within Set Sum of Squared Errors = 943.2074999999998
Vectors 7.3 1.5 10.9 is belong to cluster:0
Vectors 4.2 11.2 2.7 is belong to cluster:0
Vectors 18.0 4.5 3.8 is belong to cluster:1
0.0 0.0 5.0 0
0.1 10.1 0.1 0
1.2 5.2 13.5 0
9.5 9.0 9.0 0
9.1 9.1 9.1 0
19.2 9.4 29.2 0
5.8 3.0 18.0 0
3.5 12.2 60.0 1
3.6 7.9 8.1 0 |
总结
本文关于Spark实现K-Means算法代码示例的全部内容就到这里,希望对大家有所帮助。感如有不足之处,欢迎留言指出,小编会及时回复大家并更正,希望朋友们对本站多多支持!
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/mstk/p/6925736.html
相关文章
猜你喜欢
- 服务器虚拟化技术深度科普 2025-05-27
- 服务器租用价格怎么计算?服务器租用多少钱一年? 2025-05-27
- 云服务器的“弹性”体现在哪些方面? 2025-05-27
- 刀片服务器是什么 刀片服务器的主要特点 2025-05-27
- 利用FTP和计划任务自动备份网站数据和数据库 2025-05-27
TA的动态
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
您的支持,是我们最大的动力!
热门文章
-
2025-05-27 104
-
2025-05-27 89
-
勒索软件 Akira 瞄准 VMWare 旗下软件而来:加密用户虚拟机镜像
2025-05-26 44 -
2025-05-27 100
-
2025-05-25 85
热门评论