最近使用dialog写图形自动化shell脚本, 功能很强大,功能不是非常多但是足够用。想写一篇linux下dialog的使用方法,虽然命令不多,但是写起来也需要下很大功夫,而且不一定写得更好,在网上发现一篇linux shell图形化脚本文件,于是转过来了.
liunx 下的dialog 工具是一个可以和shell脚本配合使用的文本界面下的创建对话框的工具。
每个对话框提供的输出有两种形式:
1. 将所有输出到stderr 输出,不显示到屏幕。
2. 使用退出状态码,“OK”为0,“NO”为1,\”ESC\”为255
[–colors] 解读嵌入式“\\ Z”的对话框中的特殊文本序列,序列由下面的字符 0-7, b B, u, U等,恢复正常的设置使用“\\Zn”。
[–no-shadow] 禁止阴影出现在每个对话框的底部
[–shadow] 应该是出现阴影效果[–insecure] 输入部件的密码时,明文显示不安全,使用星号来代表每个字符[–no-cancel] 设置在输入框,菜单,和复选框中,不显示“cancel”项
[–clear] 完成清屏操作。在框体显示结束后,清除框体。这个参数只能单独使用,不能和别的参数联合使用。
[–ok-label <str>] 覆盖使用“OK”按钮的标签,换做其他字符。
[–cancel-label <str>] 功能同上
[–backtitle <backtitle>] 指定的backtitle字符串显示在背景顶端。
[–begin <y> <x>] 指定对话框左上角在屏幕的上的做坐标
[–timeout <secs>] 超时(返回的错误代码),如果用户在指定的时间内没有给出相应动作,就按超时处理
[–defaultno] 使的是默认值 yes/no,使用no
[–sleep <secs>]
[–stderr] 以标准错误方式输出
[–stdout] 以标准方式输出
[–default-item <str>] 设置在一份清单,表格或菜单中的默认项目。通常在框中的第一项是默认
窗体类型:
[ –yesno ] 提供一个带有yes和no按钮的简单信息框 (是/否框)
如果没有此包请先安装
yum -y install dialog
命令示例:
1.消息框 格式:dialog – -msgbox text height width
#dialog - -title TESTING - -msgbox “this is a test “ 10 20
例子:
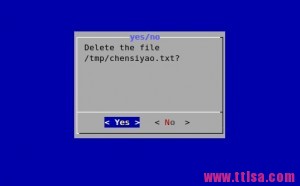
#dialog --title \"yes/no\" --no-shadow --yesno \\ \"Delete the file /tmp/chensiyao.txt?\" 10 30
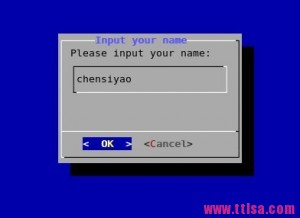
例子:
# dialog --title \"Input your name\" \\ --inputbox \"Please input your name:\" 10 30 2> /tmp/name.txt #(这里的2>是将错误信息输出重定向到了/tmp/name.txt文件中)
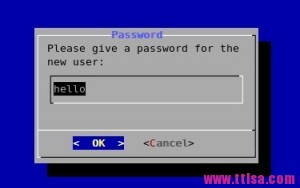
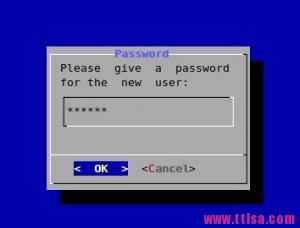
 4.密码框
4.密码框# dialog --title \"Password\" --passwordbox \\ \"Please give a password for the new user:\" 10 35
#dialog --title \"The fstab\" --textbox /etc/fstab 17 40
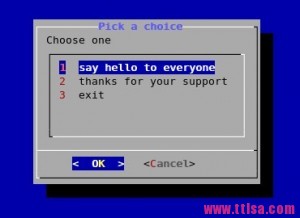
#dialog --title \"Pick a choice\" --menu \"Choose one\" 12 35 5 \\ 1 \"say hello to everyone\" 2 \"thanks for your support\" 3 \"exit\"
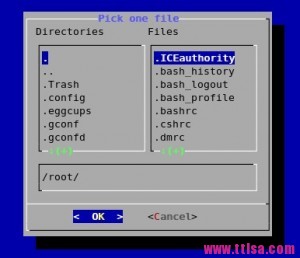
#dialog --title \"Pick one file\" --fselect /root/ 7 40
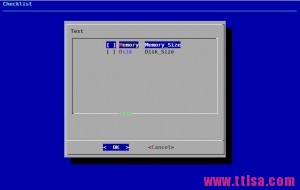
8.复选框
格式:dialog –checklist \”Test\” height width menu-height tag1 item1 tag2 item2 …
例子:
# dialog --backtitle \"Checklist\" --checklist \"Test\" 20 50 10 \\ Memory Memory_Size 1 Dsik Disk_Size 2<b></b>
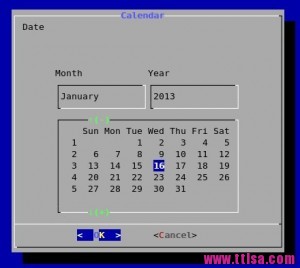
9.显示日历
格式:dialog –calendar \”Date\” height width day month year
例子:
#显示当前日期
# dialog --title \"Calendar\" --calendar \"Date\" 5 50
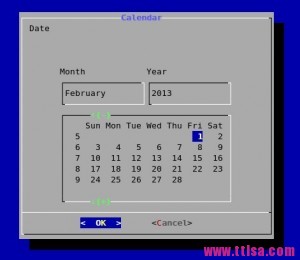
#显示指定日期
# dialog --title \"Calendar\" --calendar \"Date\" 5 50 1 2 2013
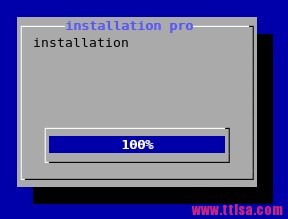
#固定进度显示
#dialog --title \"installation pro\" --gauge \"installation\" 10 30 10
#实时动度进度
#for i in {1..100} ;do echo $i;done | dialog --title \\
\"installation pro\" --gauge \"installation\" 10 30
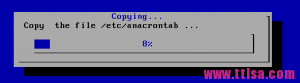
编辑一个gauge.sh 的脚本
#!/bin/bash # vim gauge.sh declare -i PERCENT=0 ( for I in /etc/*;do if [ $PERCENT -le 100 ];then cp -r $I /tmp/test 2> /dev/null echo \"XXX\" echo \"Copy the file $I ...\" echo \"XXX\" echo $PERCENT fi let PERCENT+=1 sleep 0.1 done ) | dialog --title \"coping\" --gauge \"starting to copy files...\" 6 50 0
综合应用示例:
#!/bin/bash
yesno() {
dialog --title \"First screen\" --backtitle \"Test Program\" --clear --yesno \\
\"Start this test program or not ? \\nThis decesion have to make by you. \" 16 51
# yes is 0, no is 1 , esc is 255
result=$?
if [ $result -eq 1 ] ; then
exit 1;
elif [ $result -eq 255 ]; then
exit 255;
fi
username
}
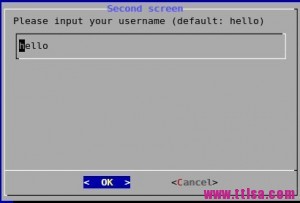
username() {
cat /dev/null >/tmp/test.username
dialog --title \"Second screen\" --backtitle \"Test Program\" --clear --inputbox \\
\"Please input your username (default: hello) \" 16 51 \"hello\" 2>/tmp/test.username
result=$?
if [ $result -eq 1 ] ; then
yesno
elif [ $result -eq 255 ]; then
exit 255;
fi
password
}
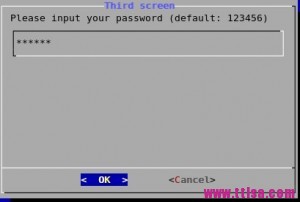
password() {
cat /dev/null >/tmp/test.password
dialog --insecure --title \"Third screen\" --backtitle \"Test Program\" --clear --passwordbox \\
\"Please input your password (default: 123456) \" 16 51 \"123456\" 2>/tmp/test.password
result=$?
if [ $result -eq 1 ] ; then
username
elif [ $result -eq 255 ]; then
exit 255;
fi
occupation
}
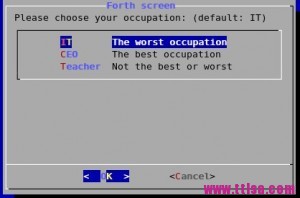
occupation() {
cat /dev/null >/tmp/test.occupation
dialog --title \"Forth screen\" --backtitle \"Test Program\" --clear --menu \\
\"Please choose your occupation: (default: IT)\" 16 51 3 \\
IT \"The worst occupation\" \\
CEO \"The best occupation\" \\
Teacher \"Not the best or worst\" 2>/tmp/test.occupation
result=$?
if [ $result -eq 1 ] ; then
password
elif [ $result -eq 255 ]; then
exit 255;
fi
finish
}
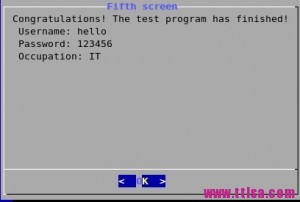
finish() {
dialog --title \"Fifth screen\" --backtitle \"Test Program\" --clear --msgbox \\
\"Congratulations! The test program has finished!\\n Username: $(cat /tmp/test.username)\\n Password: $(cat /tmp/test.password)\\n Occupation: $(cat /tmp/test.occupation)\" 16 51
result=$?
if [ $result -eq 1 ] ; then
occupation
elif [ $result -eq 255 ]; then
exit 255;
fi
}
yesno