threadlocal翻译成中文比较准确的叫法应该是:线程局部变量。
threadlocal是什么
早在jdk 1.2的版本中就提供java.lang.threadlocal,threadlocal为解决多线程程序的并发问题提供了一种新的思路。使用这个工具类可以很简洁地编写出优美的多线程程序。
当使用threadlocal维护变量时,threadlocal为每个使用该变量的线程提供独立的变量副本,所以每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会影响其它线程所对应的副本。
从线程的角度看,目标变量就象是线程的本地变量,这也是类名中“local”所要表达的意思。
所以,在java中编写线程局部变量的代码相对来说要笨拙一些,因此造成线程局部变量没有在java开发者中得到很好的普及。
threadlocal的接口方法
- threadlocal类接口很简单,只有4个方法,我们先来了解一下:
- void set(object value)设置当前线程的线程局部变量的值。
- public object get()该方法返回当前线程所对应的线程局部变量。
- public void remove()将当前线程局部变量的值删除,目的是为了减少内存的占用,该方法是jdk 5.0新增的方法。需要指出的是,当线程结束后,对应该线程的局部变量将自动被垃圾回收,所以显式调用该方法清除线程的局部变量并不是必须的操作,但它可以加快内存回收的速度。
- protected object initialvalue()返回该线程局部变量的初始值,该方法是一个protected的方法,显然是为了让子类覆盖而设计的。这个方法是一个延迟调用方法,在线程第1次调用get()或set(object)时才执行,并且仅执行1次。threadlocal中的缺省实现直接返回一个null。
值得一提的是,在jdk5.0中,threadlocal已经支持泛型,该类的类名已经变为threadlocal<t>。api方法也相应进行了调整,新版本的api方法分别是void set(t value)、t get()以及t initialvalue()。
threadlocal是如何做到为每一个线程维护变量的副本的呢?其实实现的思路很简单:在threadlocal类中有一个map,用于存储每一个线程的变量副本,map中元素的键为线程对象,而值对应线程的变量副本。我们自己就可以提供一个简单的实现版本:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
package com.test;
public class testnum {
// ①通过匿名内部类覆盖threadlocal的initialvalue()方法,指定初始值
private static threadlocal<integer> seqnum = new threadlocal<integer>() {
public integer initialvalue() {
return 0;
}
};
// ②获取下一个序列值
public int getnextnum() {
seqnum.set(seqnum.get() + 1);
return seqnum.get();
}
public static void main(string[] args) {
testnum sn = new testnum();
// ③ 3个线程共享sn,各自产生序列号
testclient t1 = new testclient(sn);
testclient t2 = new testclient(sn);
testclient t3 = new testclient(sn);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
private static class testclient extends thread {
private testnum sn;
public testclient(testnum sn) {
this.sn = sn;
}
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// ④每个线程打出3个序列值
system.out.println("thread[" + thread.currentthread().getname() + "] --> sn["
+ sn.getnextnum() + "]");
}
}
}
}
|
通常我们通过匿名内部类的方式定义threadlocal的子类,提供初始的变量值,如例子中①处所示。testclient线程产生一组序列号,在③处,我们生成3个testclient,它们共享同一个testnum实例。运行以上代码,在控制台上输出以下的结果:
thread[thread-0] –> sn[1]
thread[thread-1] –> sn[1]
thread[thread-2] –> sn[1]
thread[thread-1] –> sn[2]
thread[thread-0] –> sn[2]
thread[thread-1] –> sn[3]
thread[thread-2] –> sn[2]
thread[thread-0] –> sn[3]
thread[thread-2] –> sn[3]
考察输出的结果信息,我们发现每个线程所产生的序号虽然都共享同一个testnum实例,但它们并没有发生相互干扰的情况,而是各自产生独立的序列号,这是因为我们通过threadlocal为每一个线程提供了单独的副本。
thread同步机制的比较
threadlocal和线程同步机制相比有什么优势呢?threadlocal和线程同步机制都是为了解决多线程中相同变量的访问冲突问题。
在同步机制中,通过对象的锁机制保证同一时间只有一个线程访问变量。这时该变量是多个线程共享的,使用同步机制要求程序慎密地分析什么时候对变量进行读写,什么时候需要锁定某个对象,什么时候释放对象锁等繁杂的问题,程序设计和编写难度相对较大。
而threadlocal则从另一个角度来解决多线程的并发访问。threadlocal会为每一个线程提供一个独立的变量副本,从而隔离了多个线程对数据的访问冲突。因为每一个线程都拥有自己的变量副本,从而也就没有必要对该变量进行同步了。threadlocal提供了线程安全的共享对象,在编写多线程代码时,可以把不安全的变量封装进threadlocal。
由于threadlocal中可以持有任何类型的对象,低版本jdk所提供的get()返回的是object对象,需要强制类型转换。但jdk 5.0通过泛型很好的解决了这个问题,在一定程度地简化threadlocal的使用,代码清单 9 2就使用了jdk 5.0新的threadlocal<t>版本。
概括起来说,对于多线程资源共享的问题,同步机制采用了“以时间换空间”的方式,而threadlocal采用了“以空间换时间”的方式。前者仅提供一份变量,让不同的线程排队访问,而后者为每一个线程都提供了一份变量,因此可以同时访问而互不影响。
spring使用threadlocal解决线程安全问题我们知道在一般情况下,只有无状态的bean才可以在多线程环境下共享,在spring中,绝大部分bean都可以声明为singleton作用域。就是因为spring对一些bean(如requestcontextholder、transactionsynchronizationmanager、localecontextholder等)中非线程安全状态采用threadlocal进行处理,让它们也成为线程安全的状态,因为有状态的bean就可以在多线程中共享了。
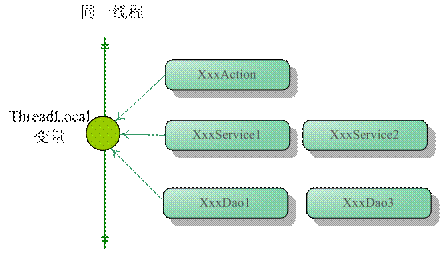
一般的web应用划分为展现层、服务层和持久层三个层次,在不同的层中编写对应的逻辑,下层通过接口向上层开放功能调用。在一般情况下,从接收请求到返回响应所经过的所有程序调用都同属于一个线程,如图9‑2所示:
通通透透理解threadlocal
同一线程贯通三层这样你就可以根据需要,将一些非线程安全的变量以threadlocal存放,在同一次请求响应的调用线程中,所有关联的对象引用到的都是同一个变量。
下面的实例能够体现spring对有状态bean的改造思路:
代码清单3 testdao:非线程安全
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
package com.test;
import java.sql.connection;
import java.sql.sqlexception;
import java.sql.statement;
public class testdao {
private connection conn;// ①一个非线程安全的变量
public void addtopic() throws sqlexception {
statement stat = conn.createstatement();// ②引用非线程安全变量
// …
}
}
|
由于①处的conn是成员变量,因为addtopic()方法是非线程安全的,必须在使用时创建一个新topicdao实例(非singleton)。下面使用threadlocal对conn这个非线程安全的“状态”进行改造:
代码清单4 testdao:线程安全
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
package com.test;
import java.sql.connection;
import java.sql.sqlexception;
import java.sql.statement;
public class testdaonew {
// ①使用threadlocal保存connection变量
private static threadlocal<connection> connthreadlocal = new threadlocal<connection>();
public static connection getconnection() {
// ②如果connthreadlocal没有本线程对应的connection创建一个新的connection,
// 并将其保存到线程本地变量中。
if (connthreadlocal.get() == null) {
connection conn = getconnection();
connthreadlocal.set(conn);
return conn;
} else {
return connthreadlocal.get();// ③直接返回线程本地变量
}
}
public void addtopic() throws sqlexception {
// ④从threadlocal中获取线程对应的connection
statement stat = getconnection().createstatement();
}
}
|
不同的线程在使用topicdao时,先判断connthreadlocal.get()是否是null,如果是null,则说明当前线程还没有对应的connection对象,这时创建一个connection对象并添加到本地线程变量中;如果不为null,则说明当前的线程已经拥有了connection对象,直接使用就可以了。这样,就保证了不同的线程使用线程相关的connection,而不会使用其它线程的connection。因此,这个topicdao就可以做到singleton共享了。
当然,这个例子本身很粗糙,将connection的threadlocal直接放在dao只能做到本dao的多个方法共享connection时不发生线程安全问题,但无法和其它dao共用同一个connection,要做到同一事务多dao共享同一connection,必须在一个共同的外部类使用threadlocal保存connection。
connectionmanager.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
package com.test;
import java.sql.connection;
import java.sql.drivermanager;
import java.sql.sqlexception;
public class connectionmanager {
private static threadlocal<connection> connectionholder = new threadlocal<connection>() {
@override
protected connection initialvalue() {
connection conn = null;
try {
conn = drivermanager.getconnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test", "username",
"password");
} catch (sqlexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
return conn;
}
};
public static connection getconnection() {
return connectionholder.get();
}
public static void setconnection(connection conn) {
connectionholder.set(conn);
}
}
|
java.lang.threadlocal<t>的具体实现
那么到底threadlocal类是如何实现这种“为每个线程提供不同的变量拷贝”的呢?先来看一下threadlocal的set()方法的源码是如何实现的:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
/**
* sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialvalue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(t value) {
thread t = thread.currentthread();
threadlocalmap map = getmap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createmap(t, value);
}
|
在这个方法内部我们看到,首先通过getmap(thread t)方法获取一个和当前线程相关的threadlocalmap,然后将变量的值设置到这个threadlocalmap对象中,当然如果获取到的threadlocalmap对象为空,就通过createmap方法创建。
线程隔离的秘密,就在于threadlocalmap这个类。threadlocalmap是threadlocal类的一个静态内部类,它实现了键值对的设置和获取(对比map对象来理解),每个线程中都有一个独立的threadlocalmap副本,它所存储的值,只能被当前线程读取和修改。threadlocal类通过操作每一个线程特有的threadlocalmap副本,从而实现了变量访问在不同线程中的隔离。因为每个线程的变量都是自己特有的,完全不会有并发错误。还有一点就是,threadlocalmap存储的键值对中的键是this对象指向的threadlocal对象,而值就是你所设置的对象了。
为了加深理解,我们接着看上面代码中出现的getmap和createmap方法的实现:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
/**
* get the map associated with a threadlocal. overridden in
* inheritablethreadlocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @return the map
*/
threadlocalmap getmap(thread t) {
return t.threadlocals;
}
/**
* create the map associated with a threadlocal. overridden in
* inheritablethreadlocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @param firstvalue value for the initial entry of the map
* @param map the map to store.
*/
void createmap(thread t, t firstvalue) {
t.threadlocals = new threadlocalmap(this, firstvalue);
}
|
接下来再看一下threadlocal类中的get()方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
/**
* returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
* thread-local variable. if the variable has no value for the
* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
* by an invocation of the {@link #initialvalue} method.
*
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
public t get() {
thread t = thread.currentthread();
threadlocalmap map = getmap(t);
if (map != null) {
threadlocalmap.entry e = map.getentry(this);
if (e != null)
return (t)e.value;
}
return setinitialvalue();
}
|
再来看setinitialvalue()方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
/**
* variant of set() to establish initialvalue. used instead
* of set() in case user has overridden the set() method.
*
* @return the initial value
*/
private t setinitialvalue() {
t value = initialvalue();
thread t = thread.currentthread();
threadlocalmap map = getmap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createmap(t, value);
return value;
}
|
获取和当前线程绑定的值时,threadlocalmap对象是以this指向的threadlocal对象为键进行查找的,这当然和前面set()方法的代码是相呼应的。
进一步地,我们可以创建不同的threadlocal实例来实现多个变量在不同线程间的访问隔离,为什么可以这么做?因为不同的threadlocal对象作为不同键,当然也可以在线程的threadlocalmap对象中设置不同的值了。通过threadlocal对象,在多线程中共享一个值和多个值的区别,就像你在一个hashmap对象中存储一个键值对和多个键值对一样,仅此而已。
小结
threadlocal是解决线程安全问题一个很好的思路,它通过为每个线程提供一个独立的变量副本解决了变量并发访问的冲突问题。在很多情况下,threadlocal比直接使用synchronized同步机制解决线程安全问题更简单,更方便,且结果程序拥有更高的并发性。
connectionmanager.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
package com.test;
import java.sql.connection;
import java.sql.drivermanager;
import java.sql.sqlexception;
public class connectionmanager {
private static threadlocal<connection> connectionholder = new threadlocal<connection>() {
@override
protected connection initialvalue() {
connection conn = null;
try {
conn = drivermanager.getconnection(
"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test", "username",
"password");
} catch (sqlexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
return conn;
}
};
public static connection getconnection() {
return connectionholder.get();
}
public static void setconnection(connection conn) {
connectionholder.set(conn);
}
}
|
后记
看到网友评论的很激烈,甚至关于threadlocalmap不是threadlocal里面的,而是thread里面的这种评论都出现了,于是有了这个后记,下面先把jdk源码贴上,源码最有说服力了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
/** * threadlocalmap is a customized hash map suitable only for
* maintaining thread local values. no operations are exported
* outside of the threadlocal class. the class is package private to
* allow declaration of fields in class thread. to help deal with
* very large and long-lived usages, the hash table entries use
* weakreferences for keys. however, since reference queues are not
* used, stale entries are guaranteed to be removed only when
* the table starts running out of space.
*/
static class threadlocalmap {...}
|
源码就是以上,这源码自然是在threadlocal里面的,有截图为证。
本文是自己在学习threadlocal的时候,一时兴起,深入看了源码,思考了此类的作用、使用范围,进而联想到对传统的synchronize共享变量线程安全的问题进行比较,而总结的博文,总结一句话就是一个是锁机制进行时间换空间,一个是存储拷贝进行空间换时间。
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的彻底理解java中的threadlocal,希望对大家有所帮助
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/lufeng20/article/details/24314381
相关文章
- 64M VPS建站:是否适合初学者操作和管理? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统中的用户注册和登录功能定制方法 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统的域名绑定与解析教程 2025-06-10
- 个人服务器网站搭建:如何选择合适的服务器提供商? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统中如何实现多语言支持? 2025-06-10
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
-
2025-05-27 84
-
2025-05-25 60
-
2025-05-25 114
-
2025-05-26 45
-
2025-05-27 85