本文实例讲述了Java基于栈方式解决汉诺塔问题。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
|
/**
* 栈方式非递归汉诺塔
* @author zy
*
*/
public class StackHanoi
{
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("快网idc测试结果:");
System.out.println("递归方式:");
hanoiNormal(3, 'A', 'B', 'C');
System.out.println();
System.out.println("非递归方式:");
hanoi(3, 'A', 'B', 'C');
}
/**
* 递归汉诺塔
* @param n
* @param A
* @param B
* @param C
*/
public static void hanoiNormal(int n, char A, char B, char C)
{
//hanoiNormal(1, A, B, C)等价于直接移动A到C( move(A,C) )
if(n==1)
{
move(A, C);
return;
}
else
{
hanoiNormal(n-1, A, C, B);
move(A, C);
hanoiNormal(n-1, B, A, C);
}
}
/**
* 非递归汉诺塔
* @param n
* @param A
* @param B
* @param C
*/
public static void hanoi(int n, char A, char B, char C)
{
//创建一个栈
StateStack s = new StateStack();
//将开始状态进栈
s.push( new State(n, A, B, C) );
//保存出栈元素
State state = null;
//出栈
while((state = s.pop()) != null)
{
//如果n为1( hanoi(1,A,B,C) ),直接移动A->C
if(state.n == 1)
{
move(state.A, state.C);
}
//如果n大于1,则按照递归的思路,先处理hanoi(n-1,A,C,B),再移动A->C(等价于hanoi(1,A,B,C) ),然后处理hanoi(n-1,B,A,C),因为是栈,所以要逆序添加
else
{
//栈结构先进后出,所以需要逆序进栈
s.push( new State(state.n-1, state.B, state.A, state.C) );
s.push( new State(1, state.A, state.B, state.C) );
s.push( new State(state.n-1, state.A, state.C, state.B) );
}
}
}
/**
* 从s到d移动盘子
*/
public static void move(char s, char d)
{
System.out.println(s+"->"+d);
}
}
//状态
class State
{
public int n;
public char A;
public char B;
public char C;
public State(int n, char A, char B, char C)
{
this.n = n;
this.A = A;
this.B = B;
this.C = C;
}
}
//栈
class StateStack
{
private State[] storage = new State[1000];
//栈顶
private int top = 0;
//入栈
public void push(State s)
{
storage[top++] = s;
}
//出栈
public State pop()
{
if(top>0)
{
return storage[--top];
}
return null;
}
}
|
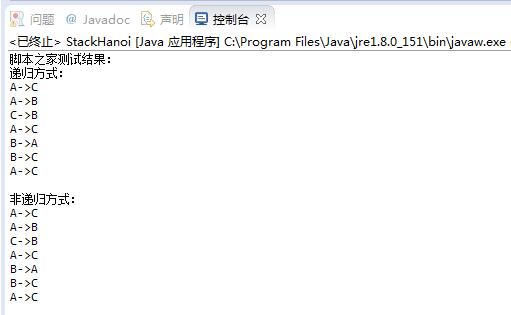
运行结果:
希望本文所述对大家java程序设计有所帮助。
原文链接:http://zy3381.iteye.com/blog/1993895
相关文章
猜你喜欢
- 64M VPS建站:能否支持高流量网站运行? 2025-06-10
- 64M VPS建站:怎样选择合适的域名和SSL证书? 2025-06-10
- 64M VPS建站:怎样优化以提高网站加载速度? 2025-06-10
- 64M VPS建站:是否适合初学者操作和管理? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统中的用户注册和登录功能定制方法 2025-06-10
TA的动态
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
您的支持,是我们最大的动力!
热门文章
-
存储区域网络(SAN)和网络附加存储(NAS)之间有何不同?适用场景和优缺点是什么?
2025-05-25 60 -
PHP中调试函数debug_backtrace的使用示例代码
2025-05-27 70 -
2025-05-29 94
-
2025-05-25 50
-
2025-06-04 98
热门评论