前言
当我们使用@discoveryclient注解的时候,会不会有如下疑问:它为什么会进行注册服务的操作,它不是应该用作服务发现的吗?下面我们就来深入的探究一下其源码。
一、springframework的lifecycle接口
要搞明白这个问题我们需要了解一下这个重要的接口:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
|
/*
* copyright 2002-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* licensed under the apache license, version 2.0 (the "license");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the license.
* you may obtain a copy of the license at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/license-2.0
*
* unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the license is distributed on an "as is" basis,
* without warranties or conditions of any kind, either express or implied.
* see the license for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the license.
*/
package org.springframework.context;
/**
* a common interface defining methods for start/stop lifecycle control.
* the typical use case for this is to control asynchronous processing.
* <b>note: this interface does not imply specific auto-startup semantics.
* consider implementing {@link smartlifecycle} for that purpose.</b>
*
* <p>can be implemented by both components (typically a spring bean defined in a
* spring context) and containers (typically a spring {@link applicationcontext}
* itself). containers will propagate start/stop signals to all components that
* apply within each container, e.g. for a stop/restart scenario at runtime.
*
* <p>can be used for direct invocations or for management operations via jmx.
* in the latter case, the {@link org.springframework.jmx.export.mbeanexporter}
* will typically be defined with an
* {@link org.springframework.jmx.export.assembler.interfacebasedmbeaninfoassembler},
* restricting the visibility of activity-controlled components to the lifecycle
* interface.
*
* <p>note that the lifecycle interface is only supported on <b>top-level singleton
* beans</b>. on any other component, the lifecycle interface will remain undetected
* and hence ignored. also, note that the extended {@link smartlifecycle} interface
* provides integration with the application context's startup and shutdown phases.
*
* @author juergen hoeller
* @since 2.0
* @see smartlifecycle
* @see configurableapplicationcontext
* @see org.springframework.jms.listener.abstractmessagelistenercontainer
* @see org.springframework.scheduling.quartz.schedulerfactorybean
*/
public interface lifecycle {
/**
* start this component.
* <p>should not throw an exception if the component is already running.
* <p>in the case of a container, this will propagate the start signal to all
* components that apply.
* @see smartlifecycle#isautostartup()
*/
void start();
/**
* stop this component, typically in a synchronous fashion, such that the component is
* fully stopped upon return of this method. consider implementing {@link smartlifecycle}
* and its {@code stop(runnable)} variant when asynchronous stop behavior is necessary.
* <p>note that this stop notification is not guaranteed to come before destruction: on
* regular shutdown, {@code lifecycle} beans will first receive a stop notification before
* the general destruction callbacks are being propagated; however, on hot refresh during a
* context's lifetime or on aborted refresh attempts, only destroy methods will be called.
* <p>should not throw an exception if the component isn't started yet.
* <p>in the case of a container, this will propagate the stop signal to all components
* that apply.
* @see smartlifecycle#stop(runnable)
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.disposablebean#destroy()
*/
void stop();
/**
* check whether this component is currently running.
* <p>in the case of a container, this will return {@code true} only if <i>all</i>
* components that apply are currently running.
* @return whether the component is currently running
*/
boolean isrunning();
}
|
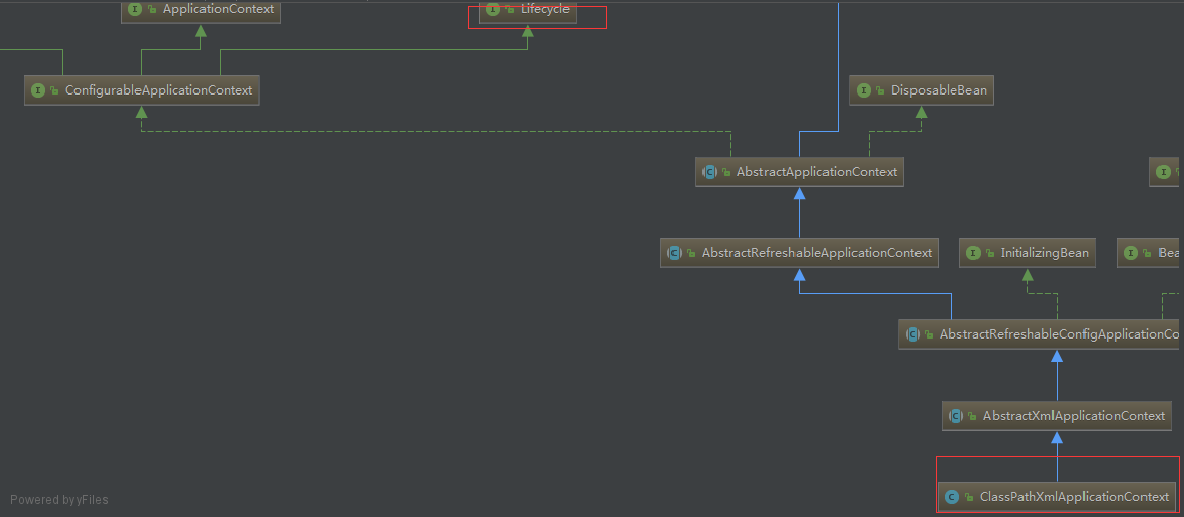
该接口定义启动/停止生命周期控制方法,当spring ioc容器启动或停止时将发送一个启动或者停止的信号通知到各个组件,因此我们可以在对应的方法里做我们想要的事情。我们可以通过类图发现我们常用的classpathxmlapplicationcontext类就实现了该接口
下面我们来简单演示一下案例,创建类mylifecycle:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
package org.hzgj.spring.study.context;
import org.springframework.context.smartlifecycle;
public class mylifecycle implements smartlifecycle {
@override
public void start() {
system.out.println("mylifecycle start ....");
}
@override
public void stop() {
system.out.println("mylifecycle stop .....");
}
@override
public boolean isrunning() {
return false;
}
@override
public boolean isautostartup() {
return true;
}
@override
public void stop(runnable callback) {
}
@override
public int getphase() {
system.out.println("phase");
return 10;
}
}
|
在这里我们继承smartlifecycle该接口继承了lifecycle, isrunning方法用于检测当前的组件是否处在运行状态,注意只有当isrunning返回值为false才可以运行
我们把mylifecycle配置到spring配置文件里,通过classpathxmlapplicationcontext运行 会得到如下结果:
另外在这里的getphase方法,这个是定义阶段值(可以理解为优先级,值越小对应的lifecycle越先执行)
二、discoveryclient源码探究
@enablediscoveyclient
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
/*
* copyright 2013-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* licensed under the apache license, version 2.0 (the "license");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the license.
* you may obtain a copy of the license at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/license-2.0
*
* unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the license is distributed on an "as is" basis,
* without warranties or conditions of any kind, either express or implied.
* see the license for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the license.
*/
package org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery;
import java.lang.annotation.documented;
import java.lang.annotation.elementtype;
import java.lang.annotation.inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.retention;
import java.lang.annotation.retentionpolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.target;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.import;
/**
* annotation to enable a discoveryclient implementation.
* @author spencer gibb
*/
@target(elementtype.type)
@retention(retentionpolicy.runtime)
@documented
@inherited
@import(enablediscoveryclientimportselector.class)
public @interface enablediscoveryclient {
/**
* if true, the serviceregistry will automatically register the local server.
*/
boolean autoregister() default true;
}
|
请注意 @import(enablediscoveryclientimportselector.class) 我们可以参考一下这个类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
/*
* copyright 2013-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* licensed under the apache license, version 2.0 (the "license");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the license.
* you may obtain a copy of the license at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/license-2.0
*
* unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the license is distributed on an "as is" basis,
* without warranties or conditions of any kind, either express or implied.
* see the license for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the license.
*/
package org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery;
import org.springframework.boot.bind.relaxedpropertyresolver;
import org.springframework.cloud.commons.util.springfactoryimportselector;
import org.springframework.core.ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.annotationattributes;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.order;
import org.springframework.core.env.configurableenvironment;
import org.springframework.core.env.environment;
import org.springframework.core.env.mappropertysource;
import org.springframework.core.type.annotationmetadata;
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.arrays;
import java.util.linkedhashmap;
import java.util.list;
/**
* @author spencer gibb
*/
@order(ordered.lowest_precedence - 100)
public class enablediscoveryclientimportselector
extends springfactoryimportselector<enablediscoveryclient> {
@override
public string[] selectimports(annotationmetadata metadata) {
string[] imports = super.selectimports(metadata);
annotationattributes attributes = annotationattributes.frommap(
metadata.getannotationattributes(getannotationclass().getname(), true));
boolean autoregister = attributes.getboolean("autoregister");
if (autoregister) {
list<string> importslist = new arraylist<>(arrays.aslist(imports));
importslist.add("org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.autoserviceregistrationconfiguration");
imports = importslist.toarray(new string[0]);
} else {
environment env = getenvironment();
if(configurableenvironment.class.isinstance(env)) {
configurableenvironment configenv = (configurableenvironment)env;
linkedhashmap<string, object> map = new linkedhashmap<>();
map.put("spring.cloud.service-registry.auto-registration.enabled", false);
mappropertysource propertysource = new mappropertysource(
"springclouddiscoveryclient", map);
configenv.getpropertysources().addlast(propertysource);
}
}
return imports;
}
@override
protected boolean isenabled() {
return new relaxedpropertyresolver(getenvironment()).getproperty(
"spring.cloud.discovery.enabled", boolean.class, boolean.true);
}
@override
protected boolean hasdefaultfactory() {
return true;
}
}
|
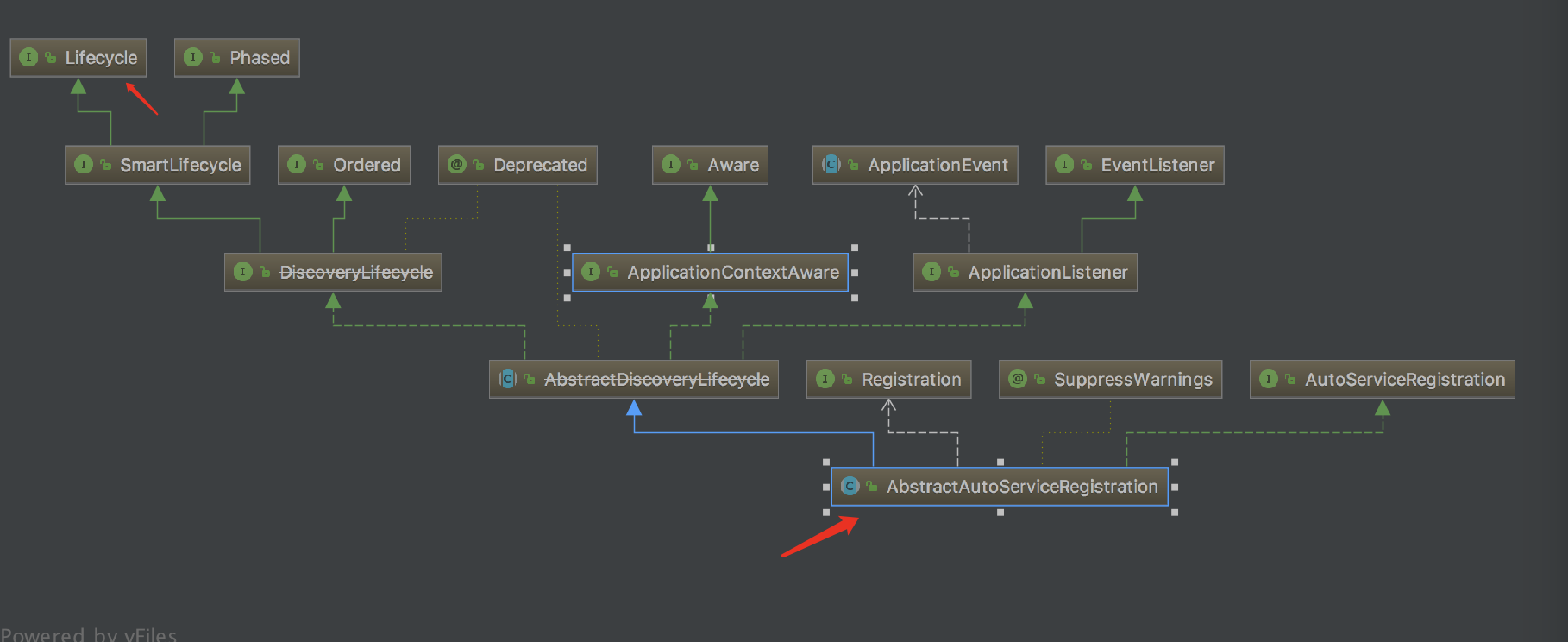
这个类重写的方法来自于接口 importselector,我们可以根据 if(autoregister)下的代码追踪到类:org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.abstractautoserviceregistration ,我们来看一下结构图:
我们可以得知这个类实现了lifecycle接口,那么我们看一看start方法,此方法在它的父类abstractdiscoverylifecycle里:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
|