本文实例讲述了java实现指定线程执行顺序的三种方式。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
方法一:通过共享对象锁加上可见变量来实现。
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
public class myservice {
private volatile int ordernum = 1;
public synchronized void methoda() {
try {
while (ordernum != 1) {
wait();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
system.out.println("aaaaa");
}
ordernum = 2;
notifyall();
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
public synchronized void methodb() {
try {
while (ordernum != 2) {
wait();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
system.out.println("bbbbb");
}
ordernum = 3;
notifyall();
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
public synchronized void methodc() {
try {
while (ordernum != 3) {
wait();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
system.out.println("ccccc");
}
ordernum = 1;
notifyall();
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
|
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import service.myservice;
public class threadaa extends thread {
private myservice dbtools;
public threadaa(myservice dbtools) {
super();
this.dbtools = dbtools;
}
@override
public void run() {
dbtools.methoda();
}
}
|
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import service.myservice;
public class threadbb extends thread {
private myservice dbtools;
public threadbb(myservice dbtools) {
super();
this.dbtools = dbtools;
}
@override
public void run() {
dbtools.methodb();
}
}
|
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
import service.myservice;
public class threadcc extends thread {
private myservice dbtools;
public threadcc(myservice dbtools) {
this.dbtools = dbtools;
}
@override
public void run() {
dbtools.methodc();
}
}
|
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import extthread.threadcc;
import service.myservice;
import extthread.threadaa;
import extthread.threadbb;
public class run {
public static void main(string[] args) {
myservice myservice = new myservice();
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
threadbb output = new threadbb(myservice);
output.start();
threadaa input = new threadaa(myservice);
input.start();
threadcc threadcc = new threadcc(myservice);
threadcc.start();
}
}
}
|
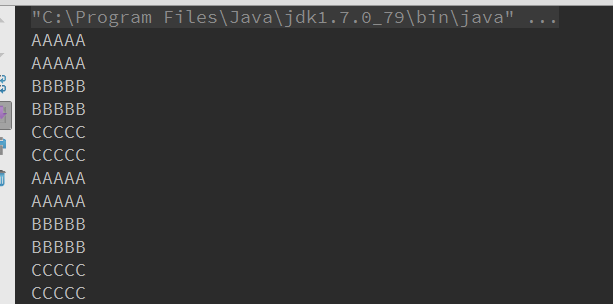
执行结果:
可以看到线程的启动按顺序执行了。共享对象锁,可以保证每个方法只能同时有一个线程进入,配合wait和notifyall方法,可以启动或者唤醒线程。
方法二:通过主线程join()
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
class t11 extends thread {
public void run() {
system.out.println("in t1");
}
}
class t22 extends thread {
public void run() {
system.out.println("in t2");
}
}
class t33 extends thread {
public void run() {
system.out.println("in t3");
}
}
public class test2 {
public static void main(string[] args) throws interruptedexception {
t11 t1 = new t11();
t22 t2 = new t22();
t33 t3 = new t33();
t1.start();
t1.join();
t2.start();
t2.join();
t3.start();
}
}
|
方法三:通过线程执行时join()
?
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
class t1 extends thread {
public void run(){
random random = new random();
try {
thread.sleep(random.nextint(1000));
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
system.out.println("in t1");
}
}
class t2 extends thread{
private thread thread;
public t2(thread thread) {
this.thread = thread;
}
public void run(){
try {
thread.join();
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
system.out.println("in t2");
}
}
class t3 extends thread{
private thread thread;
public t3(thread thread) {
this.thread = thread;
}
public void run(){
try {
thread.join();
} catch (interruptedexception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
system.out.println("in t3");
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(string[] args) throws interruptedexception {
t1 t1 = new t1();
t2 t2 = new t2(t1);
t3 t3 = new t3(t2);
t2.start();
t1.start();
t3.start();
}
}
|
希望本文所述对大家java程序设计有所帮助。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/difffate/article/details/63684290
相关文章
猜你喜欢
- 个人服务器网站搭建:如何选择合适的服务器提供商? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统中如何实现多语言支持? 2025-06-10
- 64M VPS建站:如何选择最适合的网站建设平台? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET本地开发时常见的配置错误及解决方法? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统的数据库备份与恢复操作指南 2025-06-10
TA的动态
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
您的支持,是我们最大的动力!
热门文章
-
2025-05-25 52
-
2025-05-25 85
-
2025-05-25 32
-
2025-05-27 85
-
2025-06-04 18
热门评论