上节探讨了批量新增数据,这节探讨批量更新数据两种写法的效率问题。
实现方式有两种,
一种用for循环通过循环传过来的参数集合,循环出n条sql,
另一种 用mysql的case when 条件判断变相的进行批量更新
下面进行实现。
注意第一种方法要想成功,需要在db链接url后面带一个参数 &allowmultiqueries=true
即:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysqltest?characterencoding=utf-8&allowmultiqueries=true
其实这种东西写过来写过去就是差不多一样的代码,不做重复的赘述,直接上代码。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
|
<!-- 这次用resultmap接收输出结果 -->
<select id="findbyname" parametertype="string" resultmap="customermap">
select * from t_customer where c_name like concat('%', #{name},'%') order by c_cerono limit 0,100
</select>
<!-- 批量更新第一种方法,通过接收传进来的参数list进行循环着组装sql -->
<update id="batchupdate" parametertype="java.util.map">
<!-- 接收list参数,循环着组装sql语句,注意for循环的写法
separator=";" 代表着每次循环完,在sql后面放一个分号
item="cus" 循环list的每条的结果集
collection="list" list 即为 map传过来的参数key -->
<foreach collection="list" separator=";" item="cus">
update t_customer set
c_name = #{cus.name},
c_age = #{cus.age},
c_sex = #{cus.sex},
c_cerono = #{cus.cerono},
c_cerotype = #{cus.cerotype}
where id = #{cus.id}
</foreach>
</update>
<!-- 批量更新第二种方法,通过 case when语句变相的进行批量更新 -->
<update id="batchupdatecasewhen" parametertype="java.util.map">
update t_customer
<trim prefix="set" suffixoverrides=",">
<!-- 拼接case when 这是一种写法 -->
<!--<foreach collection="list" separator="" item="cus" open="c_age = case id" close="end, ">-->
<!--when #{cus.id} then #{cus.age}-->
<!--</foreach>-->
<!-- 拼接case when 这是另一种写法,这种写着更专业的感觉 -->
<trim prefix="c_name =case" suffix="end,">
<foreach collection="list" item="cus">
<if test="cus.name!=null">
when id=#{cus.id} then #{cus.name}
</if>
</foreach>
</trim>
<trim prefix="c_age =case" suffix="end,">
<foreach collection="list" item="cus">
<if test="cus.age!=null">
when id=#{cus.id} then #{cus.age}
</if>
</foreach>
</trim>
<trim prefix="c_sex =case" suffix="end,">
<foreach collection="list" item="cus">
<if test="cus.sex!=null">
when id=#{cus.id} then #{cus.sex}
</if>
</foreach>
</trim>
<trim prefix="c_cerono =case" suffix="end,">
<foreach collection="list" item="cus">
<if test="cus.cerono!=null">
when id=#{cus.id} then #{cus.cerono}
</if>
</foreach>
</trim>
<trim prefix="c_cerotype =case" suffix="end,">
<foreach collection="list" item="cus">
<if test="cus.cerotype!=null">
when id=#{cus.id} then #{cus.cerotype}
</if>
</foreach>
</trim>
</trim>
<where>
<foreach collection="list" separator="or" item="cus">
id = #{cus.id}
</foreach>
</where>
</update>
|
接口
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
list<customer> findbyname(string name);
int batchupdate(map<string,object> param);
int batchupdatecasewhen(map<string,object> param);
|
实现类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
/**
* 用于更新时,获取更新数据
* @param name
* @return
*/
public list<customer> findbyname(string name) {
sqlsession sqlsession = null;
try {
sqlsession = sqlsessionutil.getsqlsession();
return sqlsession.selectlist("customer.findbyname", name);
} catch (exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
} finally {
sqlsessionutil.closesession(sqlsession);
}
return new arraylist<customer>();
}
/**
* 批量更新第一种方式
* @param param
* @return
*/
public int batchupdate(map<string,object> param) {
return bathupdate("customer.batchupdate",param);
}
/**
* 批量更新第二种方式
* @param param
* @return
*/
public int batchupdatecasewhen(map<string,object> param) {
return bathupdate("customer.batchupdatecasewhen",param);
}
/**
* 公共部分提出
* @param statementid
* @param param
* @return
*/
private int bathupdate(string statementid,map param){
sqlsession sqlsession = null;
try {
sqlsession = sqlsessionutil.getsqlsession();
int key = sqlsession.update(statementid, param);
// commit
sqlsession.commit();
return key;
} catch (exception e) {
sqlsession.rollback();
e.printstacktrace();
} finally {
sqlsessionutil.closesession(sqlsession);
}
return 0;
}
|
测试前准备 首先用上节的 批量插入,插入10000条数据以备下面的批量更新用。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
@test
public void batchinsert() throws exception {
map<string,object> param = new hashmap<string,object>();
list<customer> list = new arraylist<customer>();
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
customer customer = new customer();
customer.setname("准备数据" + i);
customer.setage(15);
customer.setcerono("111111111111"+i);
customer.setcerotype(2);
customer.setsex(1);
list.add(customer);
}
param.put("list",list);
long start = system.currenttimemillis();
int result = customerdao.batchinsert(param);
system.out.println("耗时 : "+(system.currenttimemillis() - start));
}
|
开始进行测试效率问题。
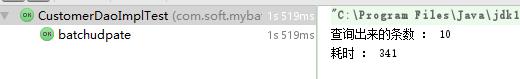
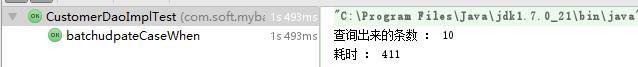
首先进行的是测试十条数据。调整查询数据为查询十条
|
1
2
3
4
|
<!-- 这次用resultmap接收输出结果 -->
<select id="findbyname" parametertype="string" resultmap="customermap">
select * from t_customer where c_name like concat('%', #{name},'%') order by c_cerono limit 0,10
</select>
|
测试类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
@test
public void batchudpate() throws exception {
map<string,object> param = new hashmap<string,object>();
param.put("list",getfindbyname("准备数据","批量更新01"));
long start = system.currenttimemillis();
customerdao.batchupdate(param);
system.out.println("耗时 : "+(system.currenttimemillis() - start));
}
@test
public void batchudpatecasewhen() throws exception {
map<string,object> param = new hashmap<string,object>();
param.put("list",getfindbyname("批量更新01","准备数据"));
long start = system.currenttimemillis();
customerdao.batchupdatecasewhen(param);
system.out.println("耗时 : "+(system.currenttimemillis() - start));
}
private list<customer> getfindbyname(string name, string change){
list<customer> list = customerdao.findbyname(name);
system.out.println("查询出来的条数 : " + list.size());
if(null != change && !"".equals(change)){
for(customer customer : list){
customer.setname(change);
}
}
return list;
}
|
第一种拼完整sql的方式耗时:
第二种case when 耗时情况:
结果可以看出,其实case when 耗时比较多。
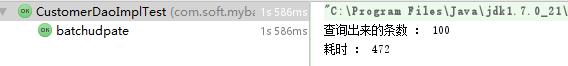
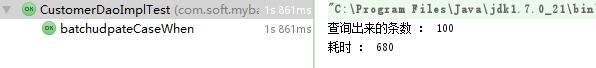
下面来加大数据量到100条;
第一种拼完整sql的方式耗时:
第二种case when 耗时情况:
结果可以看出,其实case when 耗时仍然比第一种多。
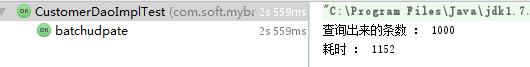
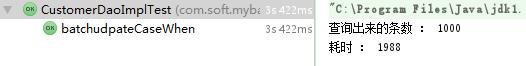
继续加大数据量到1000条
第一种拼完整sql的方式耗时:
第二种case when 耗时情况:
结果可以看出,其实case when 耗时仍然比第一种多。
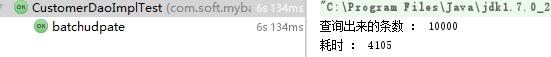
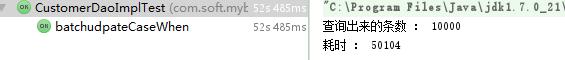
继续加大数据量到10000条
第一种拼完整sql的方式耗时:
第二种case when 耗时情况:
结果可以看出,两种方式进行批量更新,效率已经不在一个数量级了。case when明显的慢的多。
看网上有人说第一种的效率跟用代码循环着一条一条的循环着插入的效率差不多,通过测试我就有疑问了,他是怎么做到的。难道我的代码有问题?明明第一种的效率很高嘛。
第一种效率其实相当高的,因为它仅仅有一个循环体,只不过最后update语句比较多,量大了就有可能造成sql阻塞。
第二种虽然最后只会有一条更新语句,但是xml中的循环体有点多,每一个case when 都要循环一遍list集合,所以大批量拼sql的时候会比较慢,所以效率问题严重。使用的时候建议分批插入。
根据效率,安全方面综合考虑,选择适合的很重要。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持快网idc。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/xu1916659422/article/details/77971696/
相关文章
- ASP.NET本地开发时常见的配置错误及解决方法? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统的数据库备份与恢复操作指南 2025-06-10
- 个人网站服务器域名解析设置指南:从购买到绑定全流程 2025-06-10
- 个人网站搭建:如何挑选具有弹性扩展能力的服务器? 2025-06-10
- 个人服务器网站搭建:如何选择适合自己的建站程序或框架? 2025-06-10
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
-
Java中利用Alibaba开源技术EasyExcel来操作Excel表的示例代码
2025-05-29 33 -
2025-05-25 59
-
2025-05-27 26
-
选择稳定的网站服务器租用时,带宽和流量限制如何影响网站速度?
2025-05-27 102 -
2025-05-25 90