一、前言
在先了解mybatis查询之前,先大致了解下以下代码的为查询做了哪些铺垫,在这里我们要事先了解,myabtis会默认使用defaultsqlsessionfactory作为sqlsessionfactory的实现类,而sqlsession的默认实现类为defaultsqlsession
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public static sqlsessionfactory getsessionfactory() throws ioexception {
reader reader = resources.getresourceasreader("mybatis/mybatis-config.xml");
sqlsessionfactorybuilder builder = new sqlsessionfactorybuilder();
return builder.build(reader);
}
|
获取mybatis的配置文件流,交给sqlsessionfactorybuilder进行解析,在这里只会涉及到一部分,具体,请大家移步mybatis源码进行分析
解析大致步骤(以下说的配置文件,是mybatis配置数据库连接信息的那个配置文件,不是mapper.xml文件)
解析配置文件的核心类在xmlconfigbuilder类中,
代码如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
public configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new builderexception("each xmlconfigbuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseconfiguration(parser.evalnode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseconfiguration(xnode root) {
try {
// 解析properties节点信息
propertieselement(root.evalnode("properties"));
// 解析settings节点配置信息,其中二级缓存的总开关就是这里配置,当然mybatis默认是开启的,详细见configuration类中的cacheenabled属性
properties settings = settingsasproperties(root.evalnode("settings"));
loadcustomvfs(settings);
loadcustomlogimpl(settings);
// 解析别名
typealiaseselement(root.evalnode("typealiases"));
// 解析插件
pluginelement(root.evalnode("plugins"));
// 这个节点一般不进行配置,myabtis也提供了一个默认实现类defaultobjectfactory,除非自定义对象工厂实现,才需配置
objectfactoryelement(root.evalnode("objectfactory"));
objectwrapperfactoryelement(root.evalnode("objectwrapperfactory"));
reflectorfactoryelement(root.evalnode("reflectorfactory"));
settingselement(settings);
// read it after objectfactory and objectwrapperfactory issue #631
environmentselement(root.evalnode("environments"));
databaseidproviderelement(root.evalnode("databaseidprovider"));
// 处理java类型和数据库类型的转换,mybatis提供了许多默认实现,详细见typehandlerregistry类,如果需自定义,可在此节点中进行配置
typehandlerelement(root.evalnode("typehandlers"));
// 这也是一个核心的配置,mapperelement方法会对mapper.xml文件内容进行一个解析
mapperelement(root.evalnode("mappers"));
} catch (exception e) {
throw new builderexception("error parsing sql mapper configuration. cause: " + e, e);
}
}
|
解析mapper.xml文件 的类xmlmapperbuilder,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public void parse() {
// 也就是检测配置文件配置的mapper节点有没有加载到configuration类中,防止重复加载
if (!configuration.isresourceloaded(resource)) {
configurationelement(parser.evalnode("/mapper"));
configuration.addloadedresource(resource);
// 这个是绑定,mapper接口的,当处理成功,在configuration类中的mapper注册器中,会添加一个mapper
bindmapperfornamespace();
}
parsependingresultmaps();// 解析resultmap节点
parsependingcacherefs(); // 解析缓存节点,如<cache-ref/>
parsependingstatements();// 解析select|update等节点,并封装成mappedstatement类
}
|
其中bindmapperfornamespace()方法的操作会导致以下结果
在configuration类中的mapperregistry属性中添加一个mapper,结果存储在mapperregistry类的一个map中,key为mapper的class value为一个代理工厂,负责产生mapper接口代理类。
二、查询操作
当我们使用要使用mybatis进行查询操作,无非大致就是两种方式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
/**
* 通过mapper接口形式查询数据
*/
@test
public void testselectbymapper() throws ioexception {
sqlsession sqlsession = mybatisutil.getsessionfactory().opensession();
usermapper mapper = sqlsession.getmapper(usermapper.class);
user user = mapper.selectbyprimarykey(10);
system.out.println(user);
sqlsession.close();
}
/**
* 通过mapper接口的全限定名来进行查询
* @throws ioexception
*/
@test
public void testselectbystring() throws ioexception {
sqlsessionfactory sessionfactory = mybatisutil.getsessionfactory();
sqlsession sqlsession = sessionfactory.opensession();
user user = sqlsession.selectone("com.mybatis.demo.mybatisdemo.mapper.usermapper.selectbyprimarykey",10);
system.out.println(user);
sqlsession.close();
}
|
先来看第一种的分析,当我们点击getmapper进去,它会去调用configuration类中getmapper方法,就如上面介绍的解析出mapper节点后,会存储在configuration类中的mapper注册器中,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
// defaultsqlsession类
public <t> t getmapper(class<t> type) {
return configuration.<t>getmapper(type, this);
}
//configuration类
public <t> t getmapper(class<t> type, sqlsession sqlsession) {
return mapperregistry.getmapper(type, sqlsession);
}
// 最终获取mapper对象的方法,其主要是创建一个mapper代理工厂,我们都知道mybatis的mapper接口是没有实现类的,
// 但是我们直接查询是能获取数据,这里起作用的就是代理(采用的是jdk动态代理)
public <t> t getmapper(class<t> type, sqlsession sqlsession) {
final mapperproxyfactory<t> mapperproxyfactory = (mapperproxyfactory<t>) knownmappers.get(type);
if (mapperproxyfactory == null) {
throw new bindingexception("type " + type + " is not known to the mapperregistry.");
}
try {
return mapperproxyfactory.newinstance(sqlsession);
} catch (exception e) {
throw new bindingexception("error getting mapper instance. cause: " + e, e);
}
}
|
然后最终会经过代理类mapperproxy的invoke方法,进行返回结果。在这里为了更好的能理解这个类,举个例子,步骤如下
先创建一个接口,再使用一个类去实现java的jdk代理的核心接口invocationhandler,
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
public interface testmapper {
user findbyuserid(integer id);
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public class mapperproxytest implements invocationhandler {
private class<?> target;
public mapperproxytest(class<?> target) {
this.target = target;
}
public object getproxyinstances(){
return proxy.newproxyinstance(thread.currentthread().getcontextclassloader(),new class[]{target},this);
}
@override
public object invoke(object proxy, method method, object[] args) throws throwable {
if (object.class.equals(method.getdeclaringclass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
user user = new user();
user.setpassword("123");
user.setusername("李四");
user.setaddress("123");
user.setregistertime(new date());
user.setcellphone("1111111");
user.setage(25);
return user;
}
}
|
测试类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public class mappertest {
public static void main(string[] args){
mapperproxytest proxytest = new mapperproxytest(testmapper.class);
testmapper testmapper = (testmapper) proxytest.getproxyinstances();
system.out.println(testmapper.findbyuserid(10));
}
}
|
执行结果
user{id=null, username='李四', password='123', age=25, address='123', cellphone='1111111', registertime=sat mar 09 15:02:16 cst 2019}
由上面例子也可以看出最终结果是在invoke方法内,同理在mybatis中的mapperproxy的invoke方法也是负责返回最终结果的
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public object invoke(object proxy, method method, object[] args) throws throwable {
try {
if (object.class.equals(method.getdeclaringclass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isdefaultmethod(method)) {
return invokedefaultmethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (throwable t) {
throw exceptionutil.unwrapthrowable(t);
}
// 交给了mppermethod类去处理
final mappermethod mappermethod = cachedmappermethod(method);
return mappermethod.execute(sqlsession, args);
}
|
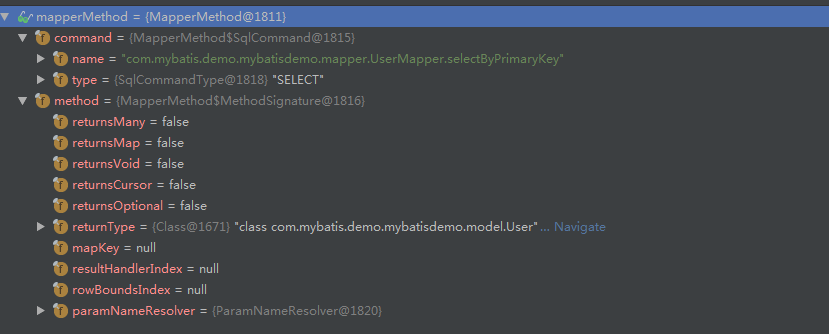
mappermethod类中有两个重要属性,也就是它的内部类,
也可以很清楚的了解到sqlcommand是用来存储当前执行方法的信息,如全限定名,还有该方法是属于select|update|delete|insert|flush的哪一种,
对于methodsignature,则是纪录该方法的一些信息,如返回值类型,参数等信息,paramnameresolver处理mapper接口中的参数,下面代码中有一个大致的介绍,以后会做一个详细的介绍,这里只贴下代码,只针对select做介绍
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
public object execute(sqlsession sqlsession, object[] args) {
object result;
switch (command.gettype()) {
case insert: {
object param = method.convertargstosqlcommandparam(args);
result = rowcountresult(sqlsession.insert(command.getname(), param));
break;
}
case update: {
object param = method.convertargstosqlcommandparam(args);
result = rowcountresult(sqlsession.update(command.getname(), param));
break;
}
case delete: {
object param = method.convertargstosqlcommandparam(args);
result = rowcountresult(sqlsession.delete(command.getname(), param));
break;
}
case select:
if (method.returnsvoid() && method.hasresulthandler()) {// 返回值为void类型,但是有resulthandler参数,并且只能有一个,不然会报错
executewithresulthandler(sqlsession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsmany()) {// 处理返回值类型为集合类型或者数组类型
result = executeformany(sqlsession, args);
} else if (method.returnsmap()) {//处理返回值类型为map类型
result = executeformap(sqlsession, args);
} else if (method.returnscursor()) {//返回值是否为cursor类型
result = executeforcursor(sqlsession, args);
} else {//其他类型
object param = method.convertargstosqlcommandparam(args);
result = sqlsession.selectone(command.getname(), param);
if (method.returnsoptional() &&
(result == null || !method.getreturntype().equals(result.getclass()))) {
result = optional.ofnullable(result);
}
}
break;
case flush:
result = sqlsession.flushstatements();
break;
default:
throw new bindingexception("unknown execution method for: " + command.getname());
}
if (result == null && method.getreturntype().isprimitive() && !method.returnsvoid()) {
throw new bindingexception("mapper method '" + command.getname()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getreturntype() + ").");
}
return result;
}
|
这里只介绍select部分中常用返回多个实例对象的情况,也就是返回值为集合类型。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
private <e> object executeformany(sqlsession sqlsession, object[] args) {
list<e> result;
// 将mapper接口的参数名称和args整成一个map结构,最后在会将值赋给sql中对应的变量
// 在3.5版本中,默认的mapper结构(假如没使用@param注解或者处于jdk1.8版本中在代码编译时加上 -parameters 参数),结构为
// param1 -> args[0] param2 -> args[1]
// arg0 -> args[0] arg1 -> args[1] mybatis之前有些版本不是arg0 而是0 1 。。数字代替。
object param = method.convertargstosqlcommandparam(args);
if (method.hasrowbounds()) {// 处理参数中带有rowbounds参数
rowbounds rowbounds = method.extractrowbounds(args);
result = sqlsession.<e>selectlist(command.getname(), param, rowbounds);
} else {// 其它情况
result = sqlsession.<e>selectlist(command.getname(), param);
}
// issue #510 collections & arrays support
// 说明返回类型不是集合list类型,而是数组类型或其它集合类型。
if (!method.getreturntype().isassignablefrom(result.getclass())) {
if (method.getreturntype().isarray()) {
return converttoarray(result);
} else {
return converttodeclaredcollection(sqlsession.getconfiguration(), result);
}
}
return result;
}
|
从上面知道,最终还是回到了sqlsession里面,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
@override
public <e> list<e> selectlist(string statement, object parameter, rowbounds rowbounds) {
try {
mappedstatement ms = configuration.getmappedstatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapcollection(parameter), rowbounds, executor.no_result_handler);
} catch (exception e) {
throw exceptionfactory.wrapexception("error querying database. cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
errorcontext.instance().reset();
}
}
|
mappedstatement存储的其实就是对每一个select|update|delete|insert 标签的解析结果
关于mappedstatement是怎么解析得来的,又是怎么存储在configuration中,可沿着以下路线进行查看
sqlsessionfactorybuilder —> build方法
xmlconfigbuilder —-> parse、parseconfiguration、mapperelement方法
xmlmapperbuilder —-> parse、parsependingstatements、parsestatementnode
mapperbuilderassistant —-> addmappedstatement
这里不做过多介绍,详情见源码
在selectlist中executor的默认实现类是,simpleexecutor,不过它还由configuration类中的一个属性决定最后的类型,
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public executor newexecutor(transaction transaction, executortype executortype) {
executortype = executortype == null ? defaultexecutortype : executortype;
executortype = executortype == null ? executortype.simple : executortype;
executor executor;
if (executortype.batch == executortype) {
executor = new batchexecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (executortype.reuse == executortype) {
executor = new reuseexecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new simpleexecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 如果cacheenabled为true,其实这个属性默认为true的,
// 则由cachingexecutor进行包装,也就是常说的装饰设计模式
if (cacheenabled) {
executor = new cachingexecutor(executor);
}
executor = (executor) interceptorchain.pluginall(executor);
return executor;
}
|
最后回到selectlist中来,由此可见,调用了cachingexecutor类中的query方法来执行。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
@override
public <e> list<e> query(mappedstatement ms, object parameterobject, rowbounds rowbounds, resulthandler resulthandler, cachekey key, boundsql boundsql)
throws sqlexception {
// 如果不为空,则启用了二级缓存
cache cache = ms.getcache();
if (cache != null) {
flushcacheifrequired(ms);
if (ms.isusecache() && resulthandler == null) {
ensurenooutparams(ms, boundsql);
@suppresswarnings("unchecked")
list<e> list = (list<e>) tcm.getobject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterobject, rowbounds, resulthandler, key, boundsql);
tcm.putobject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterobject, rowbounds, resulthandler, key, boundsql);
}
|
关于二级缓存,相信熟悉的都清楚,要想使用它,需要动两个地方,
一个是mybatis的配置文件,将cacheenabled设置为true,其实mybatis对这个属性的默认值就是true,所以二级缓存的总开关是打开的。
第二个就是在mpper.xml文件中使用 <cache/> 或<cache-ref/>
这里对缓存不做介绍。
然后调用了baseexecutor的query方法,这个类起的作用就是对一级缓存进行了操作,最终调用了simpleexecutor的doquery方法进行查询。
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,谢谢大家对快网idc的支持。
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/qm-article/p/10542187.html
相关文章
- ASP.NET自助建站系统的数据库备份与恢复操作指南 2025-06-10
- 个人网站服务器域名解析设置指南:从购买到绑定全流程 2025-06-10
- 个人网站搭建:如何挑选具有弹性扩展能力的服务器? 2025-06-10
- 个人服务器网站搭建:如何选择适合自己的建站程序或框架? 2025-06-10
- 64M VPS建站:能否支持高流量网站运行? 2025-06-10
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
-
Win7安全模式的进入方法有哪些?三种安全模式进入方法任你选择
2025-05-27 64 -
2025-06-04 53
-
2025-05-25 33
-
2025-06-04 39
-
2025-06-04 69