1 redis主从复制的概念
多机环境下,一个redis服务接收写命令,当自身数据与状态发生变化,将其复制到一个或多个redis。这种模式称为主从复制。在redis中通过命令salveof命令让执行该命令的redis复制另一个redis数据与状态。我们将主服务器称为master,从服务器称为slave。
主从复制保证了网络异常正常时,网络断开重的情况下将数据复制。网络正常时master会通过发送命令保持对slave更新,更新包括客户端的写入,key的过期或被逐出等网络异常,master与slave连接断开一段时间,slave重连上master后会尝试部分重同步,重新获取连接断开期间丢失的命令。当无法进行部分重同步,则会执行全量重同步。
2 为什么需要主从复制
为了保证数据不丢失,有时会用到持久化功能。但这样会增加磁盘IO操作。通过使用主从复制,可以替代持久化并减少IO操作,降低延迟提高性能。
主从模式下,master负责处理写,slave负责读。虽然主从同步会导致在数据存在不一致窗口,但可以增加读操作的吞吐量。主从模式避免了redis单点风险。通过副本提高系统可用性。当master挂掉,从slave中选举新的机器作为master保证系统可用。
3 主从复制配置及原理
初始化:从服务器执行完 slaveof 命令后,slave与master建立socket连接。连接建立完毕后通过ping进行心跳检测,若master正常,则返回响应。如果出现故障收不到响应,那么slave会重新尝试连接master。如果master设置了认证信息,则会再检查认证数据是否正确。如果认证失败,则会报错。
同步:当初始化完毕,master收到slave的数据同步命令后,需要判断是否执行全量同步还是部分同步。
命令传播:同步完成后,master与slave通过心跳检测判断对方是否在线。slave同时向master发送自己复制缓冲区的偏移量。master根据这些请求,判断是否向slave同步新产生的命令。slave收到同步的命令后执行,最终与master保持同步。
4 使用Lettuce在主从模式下执行命令
常用的Java Redis客户端有Jedis、Redission、Lettuce。这里将通过Lettuce来演示主从模式下的读写分离命令执行。
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
<dependency>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
<version>5.1.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
|
下面通过
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
package redis;
import io.lettuce.core.ReadFrom;
import io.lettuce.core.RedisClient;
import io.lettuce.core.RedisURI;
import io.lettuce.core.api.sync.RedisCommands;
import io.lettuce.core.codec.Utf8StringCodec;
import io.lettuce.core.masterslave.MasterSlave;
import io.lettuce.core.masterslave.StatefulRedisMasterSlaveConnection;
import org.assertj.core.util.Lists;
class MainLettuce {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<RedisURI> nodes = Lists.newArrayList(
RedisURI.create("redis://localhost:7000"),
RedisURI.create("redis://localhost:7001")
);
RedisClient redisClient = RedisClient.create();
StatefulRedisMasterSlaveConnection<String, String> connection = MasterSlave.connect(
redisClient,
new Utf8StringCodec(), nodes);
connection.setReadFrom(ReadFrom.SLAVE);
RedisCommands<String, String> redisCommand = connection.sync();
redisCommand.set("master","master write test2");
String value = redisCommand.get("master");
System.out.println(value);
connection.close();
redisClient.shutdown();
}
}
|
补充:Redis 客户端之Lettuce配置使用(基于Spring Boot 2.x)
开发环境:使用Intellij IDEA + Maven + Spring Boot 2.x + JDK 8
Spring Boot 从 2.0版本开始,将默认的Redis客户端Jedis替换问Lettuce,下面描述Lettuce的配置使用。
1.在项目的pom.xml文件下,引入Redis在Spring Boot 下的相关Jar包依赖
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
properties>
<redisson.version>3.8.2</redisson.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
2.在项目的resources目录下,在application.yml文件里添加lettuce的配置参数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
#Redis配置
spring:
redis:
database: 6 #Redis索引0~15,默认为0
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
password: #密码(默认为空)
lettuce: # 这里标明使用lettuce配置
pool:
max-active: 8 #连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
max-wait: -1ms #连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
max-idle: 5 #连接池中的最大空闲连接
min-idle: 0 #连接池中的最小空闲连接
timeout: 10000ms #连接超时时间(毫秒)
|
3.添加Redisson的配置参数读取类RedisConfig
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
package com.dbfor.redis.config;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
/**
* RedisTemplate配置
* @param connectionFactory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(LettuceConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
// 配置redisTemplate
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());//key序列化
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());//value序列化
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}
|
4.构建Spring Boot的启动类RedisApplication
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
package com.dbfor.redis;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class RedisApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RedisApplication.class);
}
}
|
5.编写测试类RedisTest
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
package com.dbfor.redis;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@Component
public class RedisTest {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
public void set() {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("test:set1", "testValue1");
redisTemplate.opsForSet().add("test:set2", "asdf");
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put("hash1", "name1", "lms1");
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put("hash1", "name2", "lms2");
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put("hash1", "name3", "lms3");
System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("test:set"));
System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForHash().get("hash1", "name1"));
}
}
|
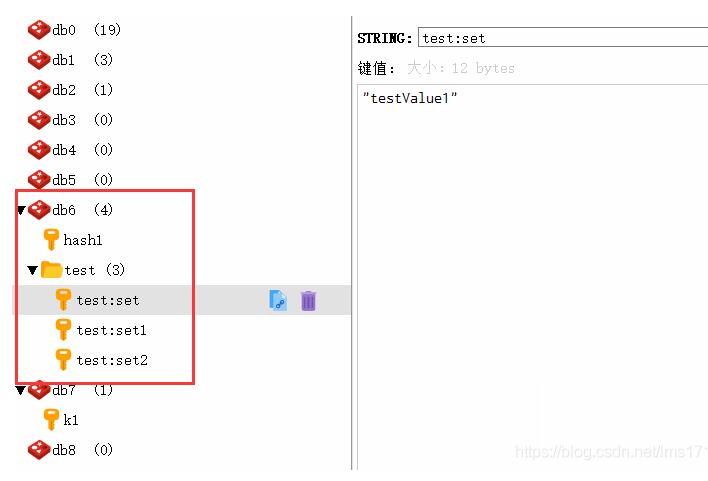
6.在Redis上查看运行结果
从上图可以看到,Lettuce配置操作数据库成功!
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持快网idc。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Revivedsun/article/details/101157571
相关文章
- ASP.NET本地开发时常见的配置错误及解决方法? 2025-06-10
- ASP.NET自助建站系统的数据库备份与恢复操作指南 2025-06-10
- 个人网站服务器域名解析设置指南:从购买到绑定全流程 2025-06-10
- 个人网站搭建:如何挑选具有弹性扩展能力的服务器? 2025-06-10
- 个人服务器网站搭建:如何选择适合自己的建站程序或框架? 2025-06-10
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全工具进行服务器漏洞扫描和修复?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用命令行工具优化Linux云服务器的Ping性能?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用Xshell连接华为云服务器,实现高效远程管理?
- 2025-07-10 怎样利用云服务器D盘搭建稳定、高效的网站托管环境?
- 2025-07-10 怎样使用阿里云的安全组功能来增强服务器防火墙的安全性?
快网idc优惠网
QQ交流群
-
2025-05-25 39
-
2025-05-29 104
-
2025-05-26 95
-
2025-05-29 95
-
2025-05-29 49